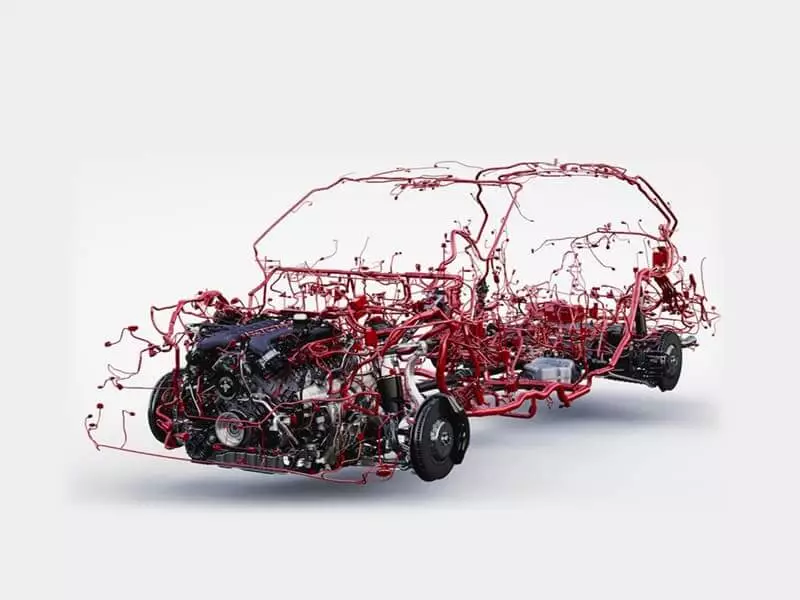
What Gauge Wire for Engine Harness?
Have you ever wondered how the wires in your car’s engine work? These seemingly ordinary wires actually form a very important system called the engine wiring harness. It is like a “nervous system” that connects the various sensors, ignition coils, fuel injectors, computers (ECU) and so on, to ensure that the entire engine can function properly.
When building or repairing an engine wiring harness, it is critical to choose the right thickness of wire (also known as Wire Gauge). If the wire is too thin, it may heat up and burn out; if the wire is too thick, it not only increases the cost, but also may be difficult to install. More importantly, improper wire gauge can affect current transmission, resulting in reduced engine performance and even safety hazards.
This article will help you figure it out:
- What thickness of wire should be used for different parts of the house?
- What standards can you refer to?
- How to avoid common wire selection mistakes?
Whether you’re an automotive modification enthusiast, an automotive repair shop, or you’re ready to get your hands dirty and build your own wiring harness. This article will help you choose the right wires to use!
What is an Engine Harness?
An Engine Harness, also known as an engine wire harness, is a collection of wires designed specifically for the engine system. It connects all the electrical components related to the engine together to ensure proper signal transmission, power supply and control commands.
An engine wiring harness usually consists of the following components:
- Multiple wires: different thicknesses (wire gauges) for transmitting different currents or signals
- Connectors (plugs, sockets): connecting various electronic components
- Protective sleeving/braiding: to protect against abrasion, high temperatures, and oils
- Accessories such as heat shrink tubing, ties, etc.: for fixing and insulation
These wires are not simply bundled together, but are designed according to a strict alignment logic and sequence. It has to adapt to the space constraints of the engine compartment, as well as resist high temperature and vibration.

What is the main role of the engine wiring harness?
Engine wiring harness is the “central nervous system” of the engine electrical system, responsible for:
- Providing power to the sensors and control unit
- Transmitting signals from sensors (e.g. temperature, pressure, speed, etc.)
- Transmitting control signals from the ECU to the ignition system, injection system and other actuators.
Why is a Wire Gauge for engine harness important?
In engine wiring harnesses, choosing the correct wire gauge is critical. Many people think that “the wire can be energized on the line”, but in fact, the thickness of the wire directly determines how much current it can carry, as well as in the high temperature and high load work safety and stability.
✅ The wire diameter affects the current carrying capacity
Each wire has its own “current-carrying capacity” (Ampacity). That is, the maximum amount of current that can safely pass through it. If the actual current passed exceeds its ampacity, the wire will heat up, soften, or even melt, causing a short circuit or fire.
In an environment like the engine compartment with high temperatures, compact spaces, and complex currents. Proper selection of wire gauge is more important than general household wiring.
Potential Issues Caused by Incorrect Wire Gauge
| Problem Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Overheating or Melting | Wire insulation may degrade or melt, increasing the risk of shorts or fire. |
| Voltage Drop | Insufficient voltage at components like injectors or sensors may cause malfunction. |
| ECU Signal Errors | Thin or improperly shielded wires can lead to inaccurate sensor readings. |
| Hard Starting | Undersized wires to starter relays or ignition coils may cause slow or failed starts. |
| Reduced Reliability | Higher chance of failure in hot or high-vibration environments. |
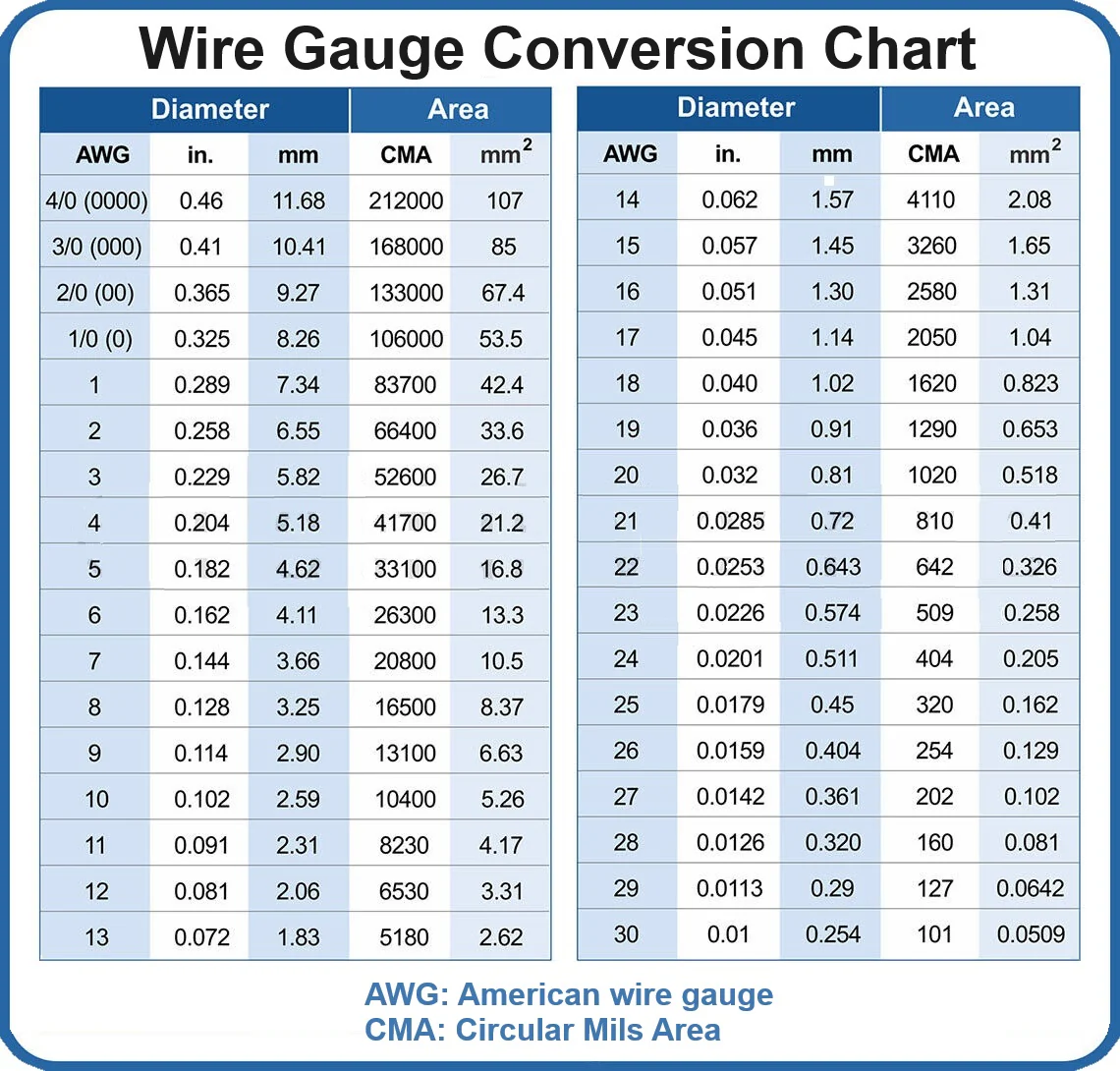
Using the AWG Standard for Wire Gauge Selection
AWG (American Wire Gauge) is a wire gauge standard widely used in North America. The smaller the value, the thicker the wire and the higher the current-carrying capacity. Example:
- 12 AWG: suitable for carrying approximately 20 amps of current (short distances)
- 18 AWG: Suitable for sensor type small current signals
- 10 AWG: suitable for starter circuits or high load devices
When making an engine wiring harness, choose a wire gauge based on conditions such as the maximum current carried by the line and the length of the wire (the longer the voltage drop, the greater the voltage drop).
In short, if the wire is too thin, it’s easy to get into trouble; if it’s too thick, it’s uneconomical and difficult to wire. Choosing just the right wire gauge is the key to professional wiring.
Wire Gauge Chart for Engine Harness
| Component | Typical Current Load | Recommended Wire Gauge (AWG) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECU Main Power Supply | 15–20A | 12 AWG | Use high-temperature rated wire |
| Fuel Injectors | 2–5A per injector | 18–20 AWG | Use uniform length for all cylinders |
| Ignition Coils | 6–10A | 16–18 AWG | Consider shielded wire if needed |
| Throttle Position Sensor | <1A | 20–22 AWG | Signal wire—keep away from EMI |
| MAP / MAF Sensors | <1A | 20–22 AWG | Use twisted pair or shielded wire |
| Crank / Cam Position Sensors | <1A | 20–22 AWG | Use shielded twisted pair |
| Alternator Signal / Exciter | 3–6A | 16–18 AWG | Use abrasion-resistant insulation |
| Starter Relay Trigger | 20–30A (relay side) | 10–12 AWG | Ensure tight terminal connections |
| Ground Wires (Sensor Returns) | <1A | 18–20 AWG | Use multiple returns for reliability |
6 Factors That Affect Wire Gauge Selection for Engine Harnesses
When choosing wires for your engine harness, it’s not as if the thicker the better, nor is it as if it looks about right. Proper wire gauge selection requires a combination of several key factors, each of which is directly related to the safety, stability and longevity of the wiring.
Factor 1. Current Load - The Most Critical Factor
How much current the wire has to carry is the primary factor in determining wire gauge. Generally speaking, the higher the current, the thicker the wire needs to be in order to effectively avoid heating or even burning. For example, if the ECU main power supply may need to carry 15-20A of current, then a wire of about 12 AWG is needed. Sensor signals are less than 1A, so 22 AWG is sufficient.
When selecting wires, engineers need to anticipate the “maximum current load” and add 20-30% redundancy on top of that for added safety.

Factor 2. Wire Length - Determines the amount of voltage drop
The longer the line, the more severe the Voltage Drop is for the same current. A voltage drop can cause the ECU or sensors to work abnormally.
As a general rule, for wiring longer than 3 meters (10 feet), consider thickening the wire gauge by one notch.
If used in the engine compartment, some wires must be routed around the engine or through the firewall, and the intervening distance should not be overlooked. Thicker gauge is required for lines longer than the standard length, or low resistance materials (e.g., high purity copper wire) should be used.
Factor 3. Operating Temperature - high thermal requirements
Engine compartment temperatures can reach 100°C or more. High temperatures further reduce the current-carrying capacity of the wire at critical wire gauge levels. Ordinary PVC insulated wires can deteriorate or even melt at high temperatures. It is therefore important to select not only the right wire gauge, but also a wire that is resistant to high temperatures, such as TXL (125°C), GXL (125°C) or SXL (150°C).
Factor 4. Conductor and Insulation Quality
- Conductor material: commonly used for multi-stranded copper wire (stranded copper), both soft and conductive, avoid using cheap aluminum wire.
- Insulation Material: Different wires (TXL, GXL, SXL) correspond to different temperature and mechanical strength levels.
- Whether tinned or not: Tinned copper wire is more reliable in humid and corrosive environments.
Multi-stranded tinned copper wires are recommended for the engine compartment, insulated with highly heat-resistant automotive-grade materials.

Factor 5. Installation Space Constraints
If the wiring space is very narrow (e.g. in areas with a high density of ECU plugs), the use of excessively thick wires may instead lead to installation difficulties. In this case, a high-temperature thin wire + parallel connection can be used to share the current.
Factor 6. Future-proofing & Safety Margin
If you anticipate upgrading your injectors, electrical system, or adding sensors at a later date, it is recommended that you allow some wiggle room in your wire selection.
For example, if you are using 2A injectors now, but may switch to higher flow 4A injectors in the future, you shouldn’t just go with 20 AWG, but should consider 18 AWG.
What are the risks associated with the wrong choice of wire gauge?
If the wire gauge is chosen wrongly, electrical faults may occur in minor cases, and in serious cases, the performance of the whole vehicle may be reduced, or even lead to safety accidents. The most common problems are heating of wires, aging or melting of insulation, which may trigger short circuits and in serious cases even lead to vehicle fire.
In addition, if too thin a wire is used for sensors or control wiring, it is prone to voltage fluctuations or signal interference. This can cause the sensors to read incorrectly or the ECU to receive incorrect data, affecting the accuracy of key control systems such as fuel injection and ignition.
In some high-current application scenarios, such as starting circuits or ignition systems, insufficient wire gauge may also lead to unstable power supply. This leads to engine starting difficulties or intermittent stalling.
Overall, the wrong wire gauge is not just “the wrong wire”, but is directly related to the reliability, safety and service life of the engine system, and should not be ignored.
Recommended Wire Types for engine harness
When selecting wire for an engine harness, not only is the gauge important, but the type of wire used is also critical. Below are a few common and widely recommended wire types:
- TXL (Thin Wall Cross-Linked Polyethylene): TXL wire is a lightweight wire with cross-linked polyethylene insulation that provides excellent resistance to high temperatures (typically up to 125°C). It is widely used in engine compartments and other automotive electrical systems because it is lightweight, easy to wire, and cost effective.
- GXL (General Cross-Linked Polyethylene): GXL is a medium-thickness wire with higher mechanical strength and greater abrasion resistance than TXL. It is suitable for applications in the engine compartment where resistance to physical wear is critical. It is also resistant to high temperatures (typically 125°C) and has good chemical resistance.
- SXL (Severe Cross-Linked Polyethylene): SXL is the heaviest version, offering the most mechanical protection and thermal stability (up to 125°C or higher). Ideal for high vibration, high temperature, and high stress environments, such as engine compartment wiring for race cars or heavy equipment.
- Other Specialty Wires (e.g. Tefzel, GPT, Marine Wire): For environments with additional requirements such as oil, corrosion or temperature extremes, higher grade materials such as Tefzel (ETFE) are recommended. These
DIY or professional customization? Linkwings gives you the answer
In the engine wiring harness production, you can choose DIY homemade, you can also choose the professional wiring harness factory customized.DIY way is less costly, suitable for enthusiasts who have some hands-on ability. However, you need to pay special attention to wire gauge selection, connector crimping quality and insulation protection.
In contrast, the products provided by professional wiring harness factory are better in terms of quality, reliability and standardization. Not only can we customize wire diameter, color coding, terminal and connector standards according to actual current, installation space and environmental requirements, but we can also ensure that the overall layout of the harness is clearer and easier to maintain.
As a dedicated wiring harness solutions provider, Linkwings is committed to providing customers with high-quality, customizable wiring harnesses. Whether it’s a harness for a lightweight race car or a heavy-duty equipment harness for a high-stress environment, we can provide the support you need to create an efficient and safe electrical system.

What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
Table of Contents Wh

What is RJ45 Connector?
Table of Contents In

Top 10 LVDS Cable Manufacturers in World 2026
Table of Contents In

How to Check Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents In