FFC vs FPC Cable:The Complete Guide to Flexible Cable
Home » FFC vs FPC Cable:The Complete Guide to Flexible Cable
In modern electronic devices, the comparison between FFC and FPC cables is a frequently discussed topic. Whether in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, or medical equipment, the selection of flexible flat cables directly impacts product performance, reliability, and cost. Many engineers and procurement personnel often wonder when faced with FFC and FPC: What are the differences between them? Where do their respective advantages and limitations lie? This is precisely the core issue this article will explore in depth.
In this comprehensive guide, we will conduct a thorough comparison of FFC and FPC—covering definitions, structures, performance characteristics, and application scenarios. Drawing on Linkwings’ practical experience in the flexible cable field, we provide genuinely valuable selection guidance to help you make more rational and forward-thinking decisions in design and procurement.
What is FFC Cable?
Definition:FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) is a type of flexible cable composed of multiple parallel conductors insulated and encapsulated in PET (polyester) or similar materials. Due to its simple structure, flexibility, and lightweight nature, it is widely used for internal connections in electronic devices.
.webp)
FFC conductors are typically made of tin-plated copper, arranged in a straight pattern with uniform spacing to ensure excellent electrical performance and mechanical stability. Common pitch specifications include 0.5mm, 1.0mm, and 2.54mm, accommodating various interface and connection requirements. Additionally, its overall thin profile enables efficient routing within limited spaces.
Compared to traditional round cables, FFC offers advantages such as superior flexibility, lightweight construction, and compact footprint. In terms of manufacturing costs, FFC is also relatively economical, making it highly suitable for high-volume applications. It is important to note that its bending endurance is limited, making it more appropriate for fixed installations or applications involving low-frequency bending.
Common Applications
Due to its high cost-effectiveness and ease of use, FFC is widely adopted in consumer electronics and office equipment. Examples include:
- Connecting moving parts in printers and scanners
- Signal transmission between LCD modules and driver boards
- Internal connections in laptops, tablets, and home appliances
- Various lightweight, space-constrained electronic devices
What is FPC Cable?
Definition: FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) refers to a flexible printed circuit board, a bendable circuit manufactured using flexible substrates. Conductors and insulating layers are formed into circuit traces through processes such as photolithography and etching. This enables high-density wiring and complex circuit connections within limited space.
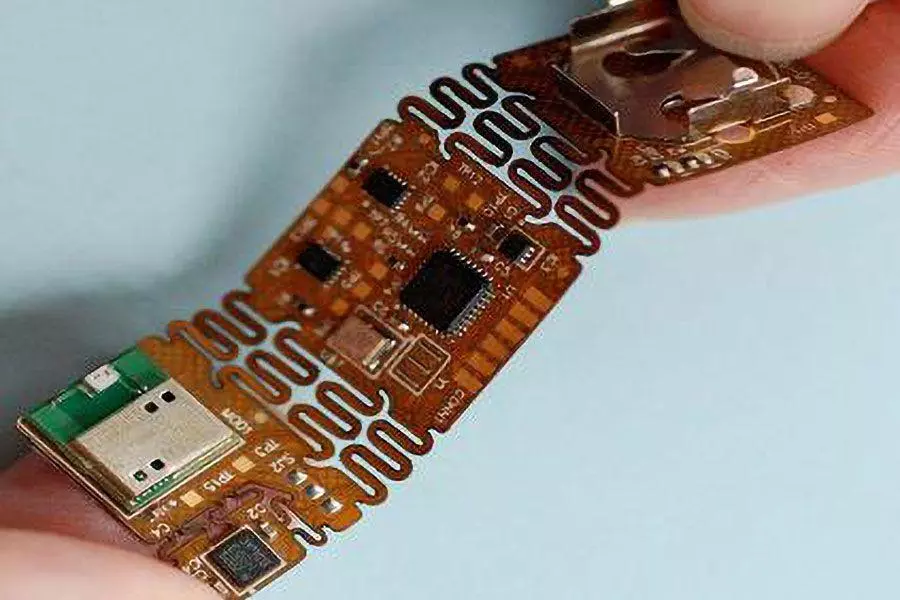
FPC typically uses polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET) as the substrate material, offering excellent heat resistance and mechanical strength. Conductive layers are predominantly etched copper foil, enabling single-layer, dual-layer, or even multi-layer routing for greater circuit design flexibility. Unlike FFC (Flat Flexible Cable), FPC allows arbitrary routing patterns without linear alignment constraints, making it ideal for complex circuit designs and highly integrated electronic products.
Additionally, FPCs offer superior flexibility and bend resistance compared to FFCs, making them suitable for connections involving repeated motion. They also exhibit excellent high-temperature resistance, maintaining stable electrical performance in harsh environments. Due to their superior electrical characteristics, FPCs deliver better signal integrity and interference resistance, making them ideal for electronic products with stringent performance requirements.
Common Applications
With their high performance and flexible design, FPCs have found widespread use in various high-end electronic devices. For example:
- Flexible circuit connections in smartphones and wearable devices
- High-density signal transmission in camera modules
- Precision electronic module connections in medical equipment
- Sensors, displays, and control units in automotive electronic systems
FFC VS FPC Cables: Key Differences Between Them
| Comparison Aspect | FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) | FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flat flexible cable with parallel conductors laminated in PET insulation | Flexible printed circuit using PI/PET substrate with etched copper traces |
| Structure | Straight, parallel conductors with fixed pitch (common 0.5mm / 1.0mm / 2.54mm) | Multi-layer routing, free layout, supports complex circuit designs |
| Manufacturing Process | Extrusion and lamination, relatively simple | Photolithography and etching, higher complexity |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, suitable for fixed or low-cycle bending | Highly flexible, suitable for repeated bending and dynamic applications |
| Electrical Performance | Cost-effective, suitable for basic signal and low-speed transmission | Superior signal integrity, suitable for high-speed and high-density transmission |
| Thickness | Relatively thicker, typically >0.2mm | Thinner, can be as low as 0.1mm or less |
| Temperature Resistance | Limited (PET material) | Excellent, with PI substrate offering high heat resistance |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost, ideal for mass production | Higher cost, more suitable for high-performance applications |
| Typical Applications | Printers, scanners, LCD modules, consumer electronics | Smartphones, camera modules, medical devices, automotive electronics |
Summary:
- FFC is more suitable for low-cost, structurally simple applications with less stringent requirements for bend endurance. Examples include home appliances, office equipment, and certain consumer products.
- FPC is ideal for high-integration, high-performance applications requiring frequent bending or high-temperature resistance. Examples include smart terminals, medical devices, and automotive electronics.
- In practical projects, engineers should select the appropriate flexible cable type based on space constraints, cost considerations, signal integrity requirements, and the operating environment.
How to Choose Between FFC and FPC?
In flexible cable applications, both FFC and FPC offer distinct advantages. However, selecting the most suitable solution based on specific requirements often poses a challenge for engineers and procurement personnel. The following aspects serve as key considerations for selection.
1. Space and Thickness Requirements
When internal device space is extremely limited and wiring must be routed between ultra-thin layers, FPC is the superior choice. Its thickness can be reduced to below 0.1mm, and it supports multi-layer designs. Conversely, in scenarios with more spacious conditions, FFC’s simple structure and straight wiring paths can meet requirements while lowering overall costs.

2. Bend Radius and Lifespan
Bend endurance is a critical factor in flexible cable design. FFC is suitable for applications with limited bending cycles, such as fixed connections between LCD modules and motherboards. In contrast, FPC offers superior bend performance, withstanding tens of thousands of bend cycles, making it ideal for dynamic applications like hinge areas in flip phones or signal transmission in robotic arms.
3. Electrical Performance (Signal Integrity, EMI Suppression)
In scenarios with lower signal frequencies and modest data transmission requirements, FFC provides stable connections at a lower cost. However, for applications involving high-speed signals, RF signals, or stringent EMI suppression demands (e.g., 5G modules, automotive radar, medical imaging equipment), FPC holds a distinct advantage. Its etched copper foil design enables superior impedance control and electromagnetic compatibility, ensuring signal integrity.
4. Cost Budget
For projects with limited budgets and basic functional requirements, FFC represents a cost-effective choice. Its simple manufacturing process and low cost make it suitable for high-volume production. Conversely, for projects demanding high reliability and complex routing, FPC—though more expensive—effectively reduces long-term maintenance and failure risks, offering greater investment value over time.

5. Industry Certification Requirements (UL, RoHS, ISO, IPC Standards)
In demanding sectors like medical, automotive, and aerospace, products must pass stringent safety and quality certifications. FPCs, typically utilizing PI (polyimide) substrates and precision manufacturing processes, more readily meet international standards such as UL, RoHS, ISO, and IPC. While FFCs can also comply with some certifications, they may face limitations in high-end industry applications.
FAQs
Q1: What is the fundamental difference between FFC and FPC?
A: FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) is a flexible ribbon cable composed of multiple parallel conductors and a PET insulating layer. It features a simple structure and low cost, making it suitable for fixed or limited bending scenarios. FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) is a flexible printed circuit board using PI/PET substrate and etched copper foil. It supports multi-layer routing, offers greater bend resistance, and delivers superior electrical performance.
Q2: Can FFC and FPC be used interchangeably?
A: In some simple applications, FFC can replace FPC. However, FPC is more suitable for high-density, high-speed signal transmission, high-temperature resistance, or frequent bending scenarios. Therefore, interchangeability depends on specific design requirements.
Q3: What are common FFC specifications?
A: Common FFC pitch (conductor spacing) specifications include 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 1.25mm, and 2.54mm. Length and pin counts can be customized per customer requirements.
Conclusion
This guide provides an in-depth comparison of FFC vs. FPC cables, examining their definitions, structures, performance characteristics, and application differences. It demonstrates that FFC is better suited for low-cost, structurally simple applications, while FPC excels in high-density routing, frequent bending, and high-performance requirements. For engineers and procurement personnel, selecting the appropriate flexible cable type can effectively enhance product reliability and cost-effectiveness.
As a professional flexible cable manufacturer, Linkwings not only offers standardized FFC and FPC products but also supports customized designs and full-process engineering assistance. We help customers identify optimal solutions for diverse application scenarios.

What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
Table of Contents Wh

What is RJ45 Connector?
Table of Contents In

Top 10 LVDS Cable Manufacturers in World 2026
Table of Contents In

How to Check Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents In