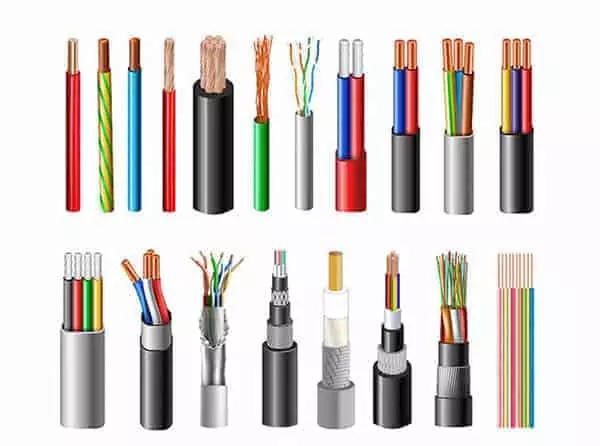
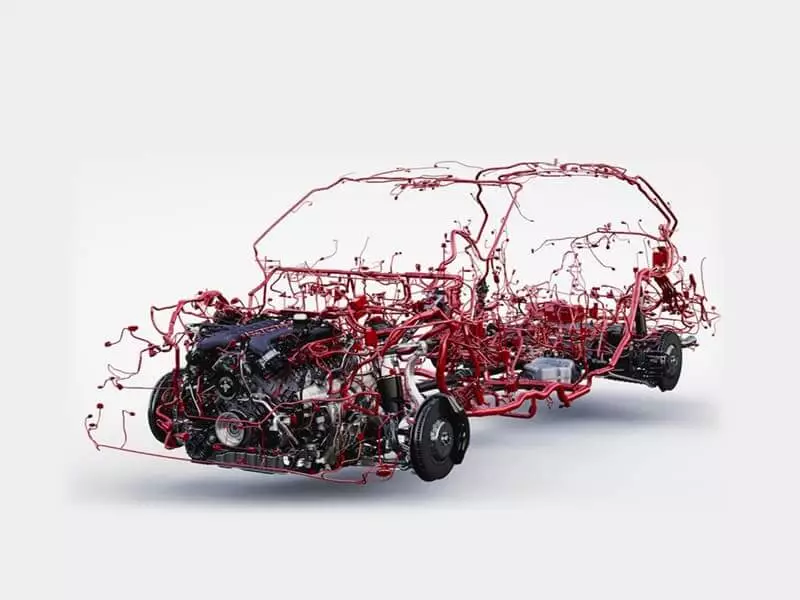
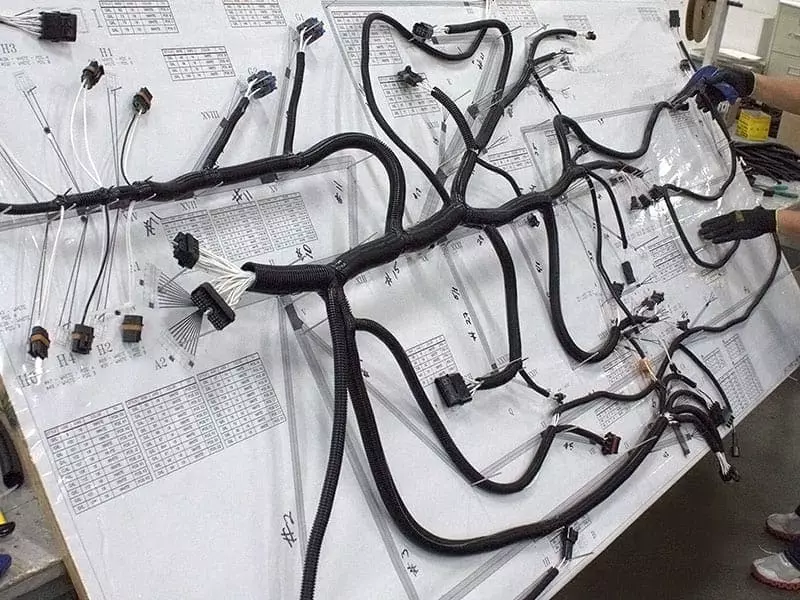
In modern manufacturing, wire harnesses have become indispensable components across automotive, home appliances, industrial equipment, medical devices, and other sectors. Functioning as the “nervous system” of equipment, they connect circuits and ensure stable transmission of signals and power.
However, many engineers, procurement personnel, and even entrepreneurs encounter a practical question when preparing projects: “How much does a wire harness actually cost?” Some discover that a small harness may cost only a few dollars, while a complex automotive main harness can reach hundreds of dollars—a gap that seems hard to comprehend.
This disparity isn’t due to arbitrary pricing but stems from multiple factors: design complexity, material selection, manufacturing processes, certification requirements, production volume, and supply chain conditions.
This article provides a professional, systematic analysis of the key factors influencing wire harness costs. It outlines realistic price ranges and procurement recommendations, empowering you to evaluate supplier quotes with clarity and identify cost-effective solutions.
Key Factors Affecting Wire Harness Cost
The price of a wire harness is not determined by a single factor but rather by the combined effect of multiple elements. The following dimensions are critical in influencing wire harness cost:
1. Design Complexity
Structural Complexity:
- If a harness consists of only a few wires and a single connector, both design and assembly difficulty are low, resulting in lower costs.
- Automotive main harnesses often incorporate hundreds of wires, dozens of branches, and hundreds of connectors, sometimes requiring multi-level routing designs. This significantly increases design expenses and assembly labor hours.
Functional Requirements:
- Is differentiation required between power lines, signal lines, and control lines?
- Does it involve high-speed data transmission (e.g., CAN bus, Ethernet cables)? These factors impose higher demands on wire gauge, shielding, and terminal selection.
Conclusion: Greater complexity directly increases engineering time, assembly time, and testing requirements, driving up costs.

2. Material Selection
Conductors:
- Common copper conductors are significantly affected by fluctuations in copper market prices.
- Tin-plated copper enhances corrosion resistance but carries a higher cost than bare copper.
- Aluminum wire offers lower cost but inferior electrical conductivity and mechanical strength compared to copper, limiting its applications.
Insulation Materials:
- PVC: Low cost and versatile, but offers limited high-temperature and chemical resistance.
- XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene): Resistant to high temperatures, oils, and abrasion, but more expensive than PVC.
- Silicone, Fluoroplastics: Suitable for high-end or specialized environments (high temperatures, strong corrosion), with significantly higher prices.
Shielding Layer:
- EMI/RFI shielding requirements add extra copper braid or aluminum foil layers, increasing material and processing costs.
Connectors and Terminals:
- Prices vary greatly across brands and grades. International brands like TE and Molex are relatively expensive.
Conclusion: Material costs account for 40–70% of wire harness pricing, making them the core cost-determining factor.
3. Manufacturing Processes and Assembly Methods
Automation vs. Manual:
- Simple linear harnesses can be processed in bulk using automated cutting machines and crimping machines, offering high efficiency and low labor costs.
- Complex harnesses often require manual routing, bundling, and sheathing installation, significantly increasing labor costs.
Termination Processes:
- Crimping is relatively inexpensive but requires dies and high-precision equipment.
- Welding or injection molding terminations offer greater durability but add extra processes and labor hours.
Inspection Processes:
- Basic testing (continuity checks) incurs lower costs.
- Rigorous testing (tensile strength tests, withstand voltage tests, 100% full inspection) increases inspection labor hours and equipment usage costs.
Conclusion: Increased process complexity and stricter inspection standards directly translate into higher labor and equipment usage expenses.
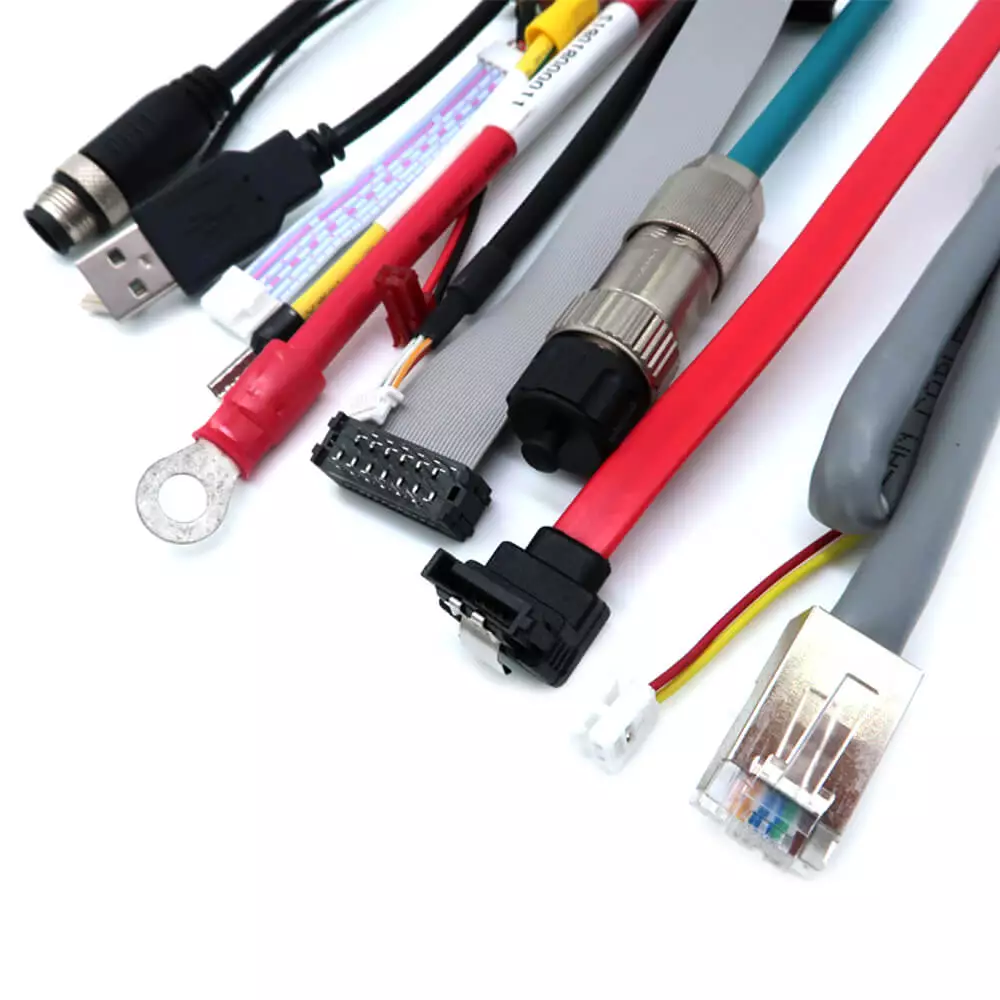

4. Production Volume and Economies of Scale
Prototyping and Small-Batch Production:
- Engineering development costs, tooling expenses, and process setup are allocated across a small number of products, resulting in extremely high unit costs.
Mass Production:
- As output increases, fixed costs are spread across a larger volume, gradually reducing the unit price.
Typical Pattern:
- Prototyping costs can be 3–5 times the unit price of mass production.
Conclusion: Order quantity is one of the decisive factors affecting unit price.
5. Certification and Standard Requirements
Industry Certifications:
UL certification, RoHS/REACH environmental compliance, IATF16949 (automotive industry), etc., all require additional testing and documentation support.
Application Domain Requirements:
- Medical devices must comply with ISO 13485, while military wiring harnesses may require MIL-SPEC standards.
- These certifications and standards entail stringent quality control and documentation tracking, inevitably increasing costs.
Conclusion: Higher certification standards and more rigorous production/testing processes directly correlate with higher unit costs for wiring harnesses.
6. Regional and Supply Chain Variations
Regional Cost Differences:
- Manufacturing costs are relatively low in China, Vietnam, India, and similar locations.
- Labor costs are higher in Europe and the Americas, but delivery speed and communication efficiency are superior.
Supply Chain Impacts:
- Fluctuations in raw material prices (copper, plastic) directly affect costs.
- Logistics, transportation, tariffs, and international trade policies also incur additional expenses.
Conclusion: Different sourcing regions and supply chain configurations significantly impact total costs and delivery cycles.
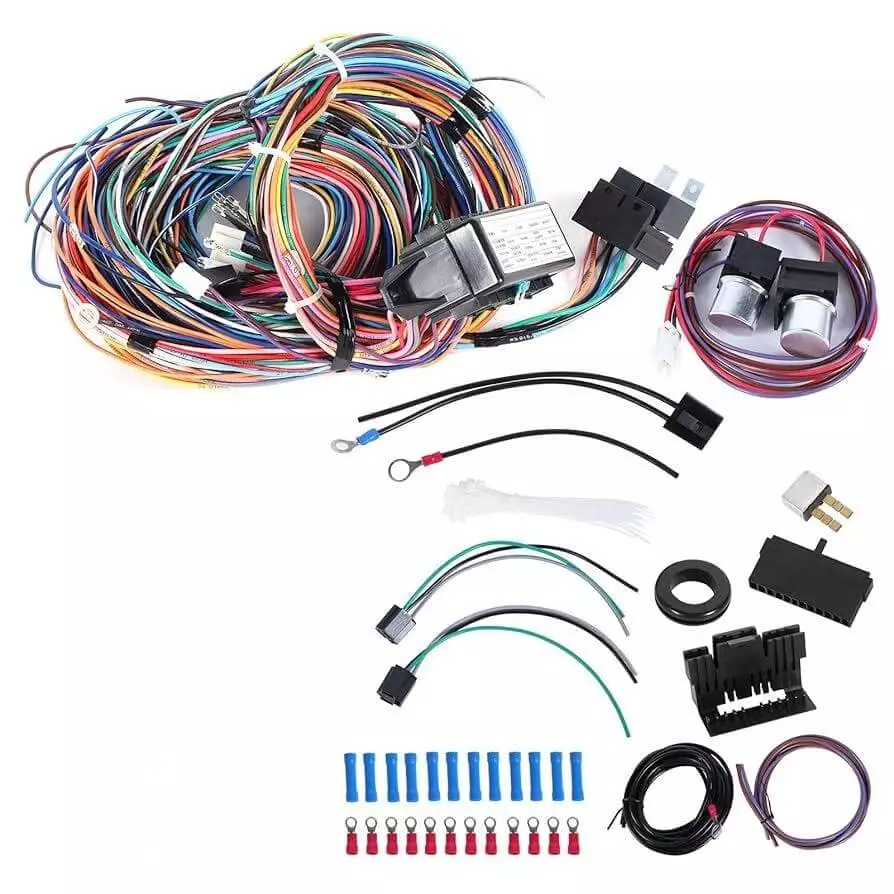

Approximate Price Range for Wire Harness Costs
Many people wish to know the approximate cost of a wire harness before requesting a quote. In reality, harness pricing varies significantly due to the combined influence of design, materials, manufacturing processes, certifications, and production volume. The following ranges serve solely as industry references to help procurement personnel and engineers make preliminary cost estimates.
1. Small, Simple Harnesses ($1–$10)
Typical Applications:
- Small appliances (electric fans, coffee makers, microwaves)
- Consumer electronics (printers, audio systems, computer peripherals)
Characteristics:
- Few wires (typically 2–10 strands)
- Standard PVC-insulated wires with common connectors
- Simple manufacturing processes, often semi-automated
Note: Low cost, but unit prices may rise to $5–$15 during small-batch customization or sample production.
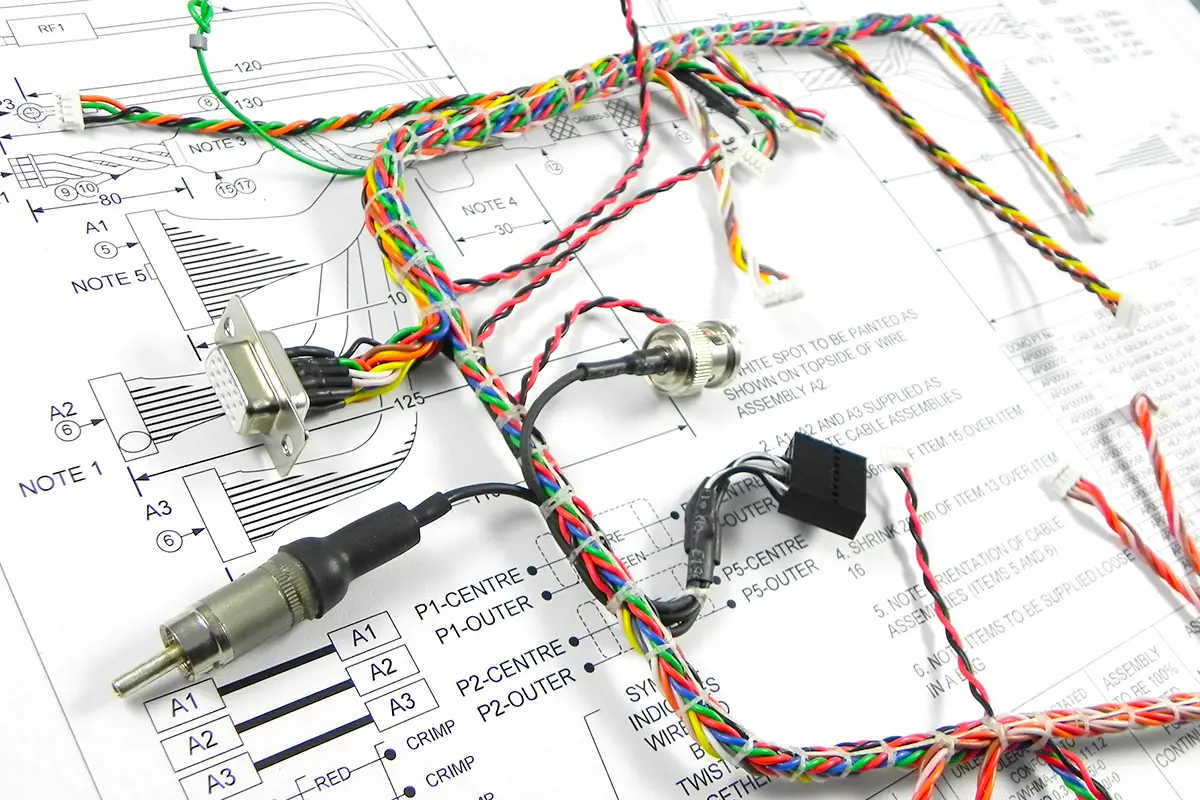
2. Medium Complexity Harnesses ($10 – $50)
Typical Applications:
- Industrial equipment
- Sub-harnesses for electric vehicles and motorcycles
- Secondary harnesses for medical devices
Characteristics:
- Higher wire count, potentially containing 20–100 conductors
- Utilizes multiple connectors and varying wire gauges
- May require partial shielding, high-temperature resistance, or flame-retardant materials
- Involves manual wiring and partial inspection processes
Note: Pricing is significantly influenced by design complexity and material variations.
3. High-Complexity Custom Wire Harnesses ($50 – Several Hundred Dollars)
Typical Applications:
- Automotive main harnesses (especially for new energy vehicles, with wire counts reaching thousands)
- Aerospace and military wire harnesses
- High-end medical equipment (e.g., signal harnesses for MRI and CT scanners)
Characteristics:
- Numerous branches and intricate routing
- Mixed wire gauges, advanced insulation and shielding materials
- High-precision connectors (brands like TE, Molex, Deutsch)
- Mandatory compliance with stringent certifications and full inspection processes
Note: These harnesses are typically custom projects, with unit costs easily exceeding $200–$500, particularly during low-volume production phases.
4. Prototyping and Sample Production Phase (3–5 times unit price)
Characteristics:
- During early project development, sample quantities are typically small (1–10 sets). Tooling, process development, and engineering costs are fully allocated to this limited production run.
- Sample unit prices are often 3–5 times higher than mass production rates.
Example:
- A wire harness with a mass production unit price of $20 may cost $60–$100 during the sample phase.
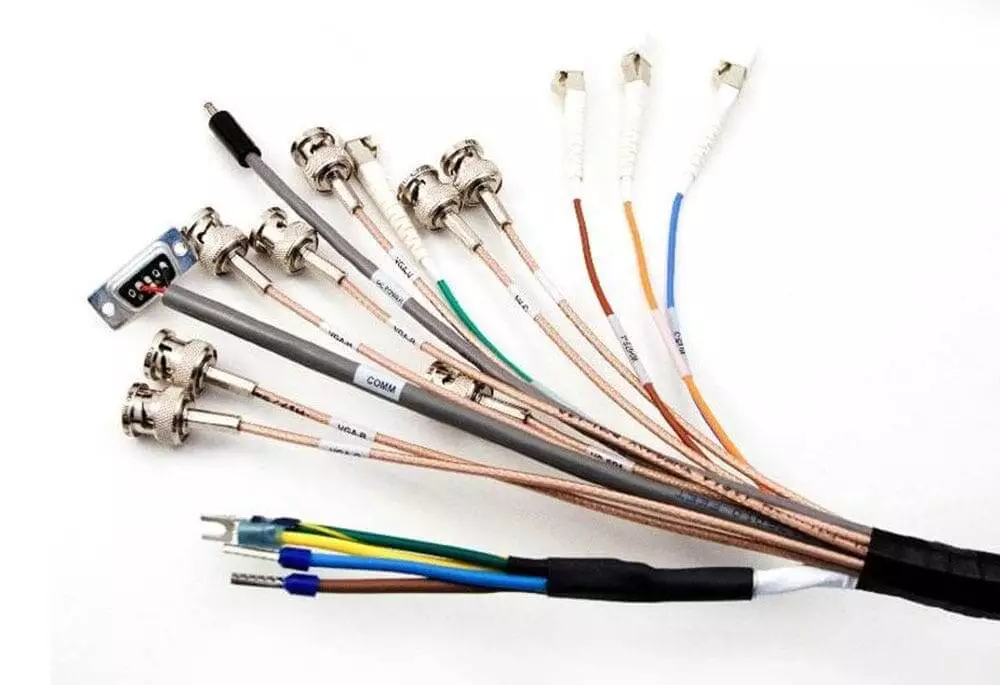

How to Obtain Accurate Wire Harness Quotes?
During actual procurement, many people find that the same wire harness can vary significantly in price across different suppliers. This is often not simply a matter of “who is cheaper,” but rather because the information provided differs, leading to substantial variations in the accuracy and comparability of quotes. To obtain a genuine, reliable wire harness quote, you must first prepare as complete technical documentation as possible. This typically includes the Bill of Materials (BOM), wire harness drawings or 3D models, wire specifications, connector models, and functional descriptions. For example, which wires are power lines versus signal lines, and the required voltage and current ratings. If the harness has special requirements—such as shielding, high-temperature resistance, oil resistance, or flame retardancy—these must also be clearly specified during the quotation request phase. Without this information, suppliers can only provide a vague “reference price,” with the actual final cost potentially exceeding the estimate by 30–50%.
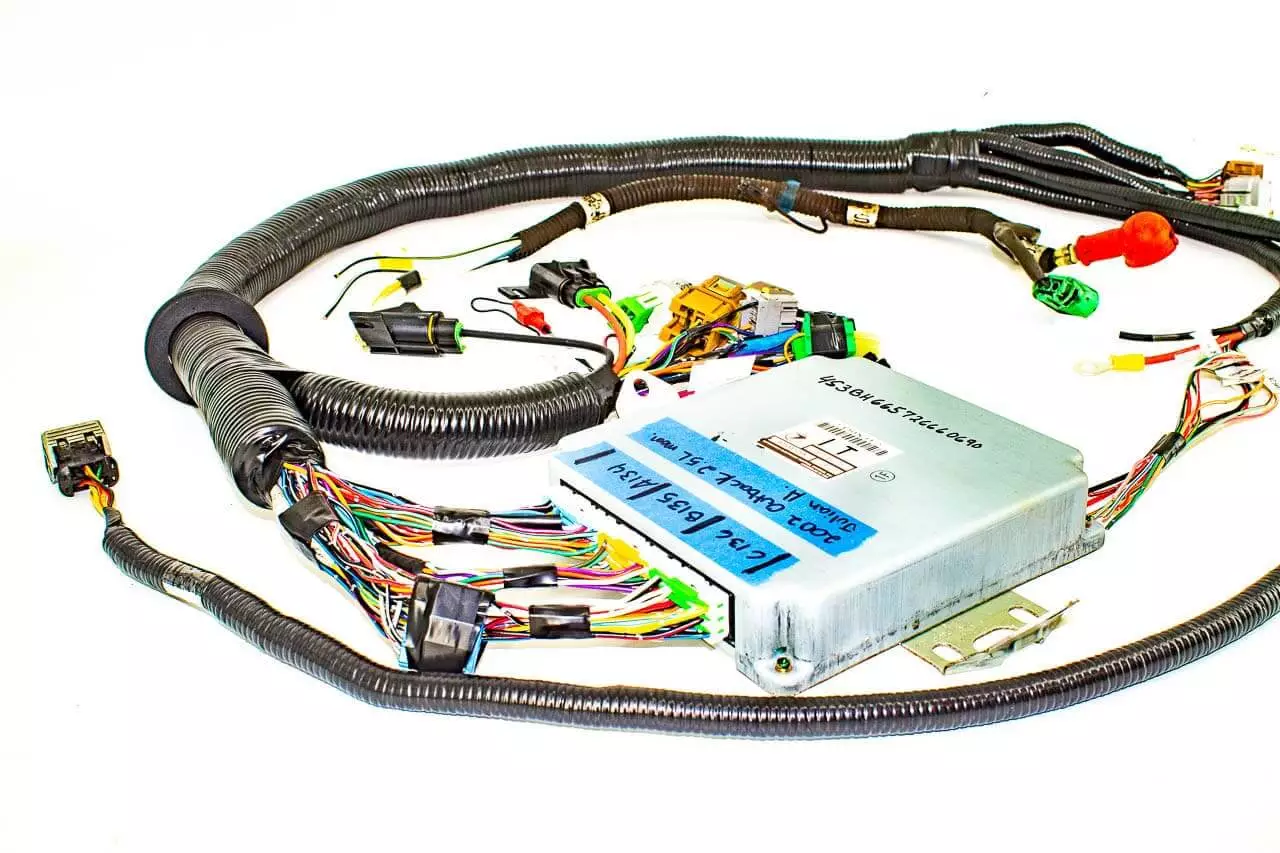

Beyond drawings and specifications, production and testing requirements also impact pricing. Many clients only request basic continuity testing, but in automotive, medical, or industrial sectors, additional requirements like withstand voltage testing, tensile strength testing, or even 100% full inspection are common. These entail extra labor and equipment costs. Compliance with certifications such as UL, IATF16949, or ISO13485 can also significantly increase expenses. Therefore, clearly communicate quality and testing standards to suppliers before requesting quotes to avoid subsequent revisions or unexpected price increases.
How Should You Judge the “Cost-Effectiveness” of a Wire Harness?
When determining whether a wire harness offers good value for money, price alone is insufficient. First, confirm that it meets the project’s performance and safety requirements—this is the fundamental prerequisite. Next, assess whether the cost structure is reasonable, avoiding both over-engineering that leads to waste and cutting corners that create hidden risks. Finally, consider the supplier’s responsiveness and service capabilities, ensuring they can provide stable support throughout the design, prototyping, and mass production phases.
In summary, a cost-effective wire harness delivers reliable long-term value at the most appropriate cost while fully meeting all requirements.

What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
Table of Contents Wh

What is RJ45 Connector?
Table of Contents In

Top 10 LVDS Cable Manufacturers in World 2026
Table of Contents In

How to Check Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents In