Automotive Wiring Harness Types: A Complete Guide for All Vehicle Applications
Home » Automotive Wiring Harness Types: A Complete Guide for All Vehicle Applications
There are many automotive wiring harness types. Different types of wiring harnesses are responsible for different functions and modules in a car.
This blog will focus on the importance of choosing the right type of automotive wiring harness, the main types of automotive wiring harness and the classification of eco-friendly types of automotive wiring harnesses depending on the application.
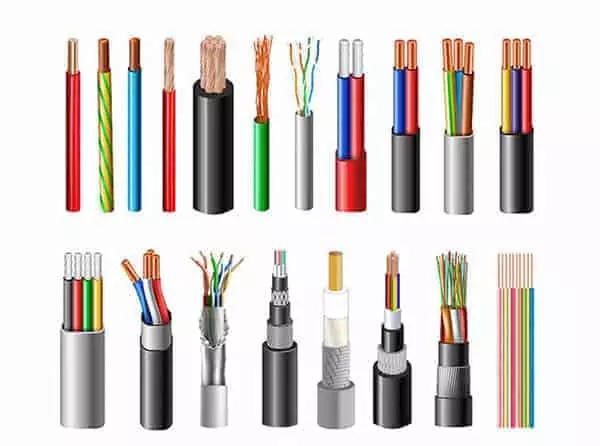
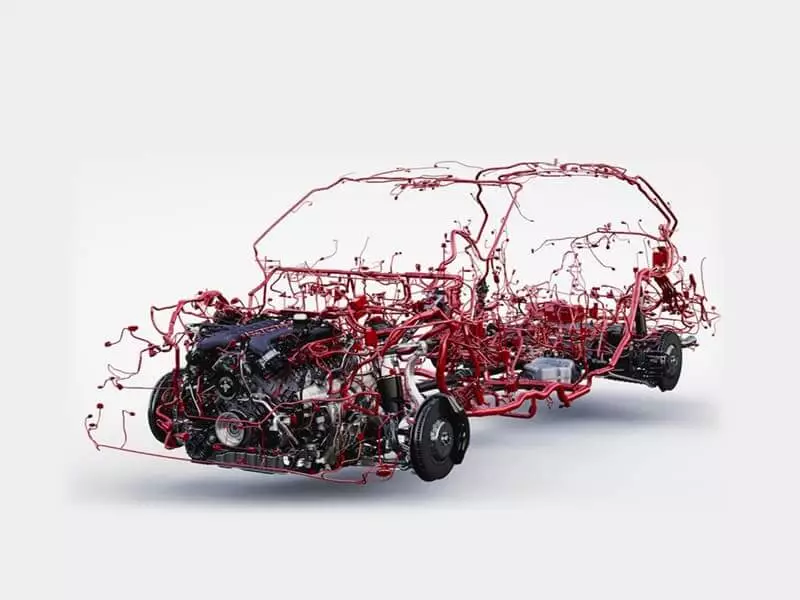
Automotive Wiring Harness, also known as automotive cable harness or cable assembly. It is a “circuit distribution system” that consists of multiple wires, cables, connectors, terminals, jackets and other components that are integrated according to the needs of the electrical system. It is like a neural network in the human body, responsible for transmitting power and signals from the vehicle’s control unit to various functional components. For example, the signal connections between the engine, lights, instrumentation, air conditioning, sensors, safety systems, etc. are all completed by the automotive wiring harness.
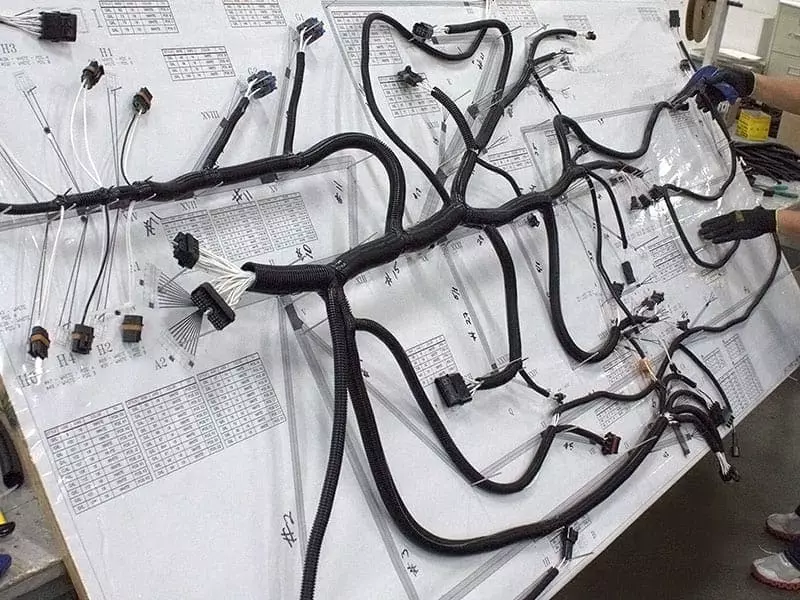
The main roles of the car wiring harness include:
- Transmitting electrical energy: connecting the battery, power module and actuator to realize power supply;
- Transmitting control signals: carrying communication commands between ECU, sensors, and switches;
- Constructing system structure: unifying and organizing all lines in the vehicle to ensure that the wiring is standardized, reliable and maintainable.
In modern vehicles, automotive wiring harness is the “central nerve” of the electrical system, related to the normal operation of all electronic systems of the vehicle. With the development of vehicle intelligence and electrification, the total length of the wiring harness of an ordinary passenger car may be more than 2 kilometers, weighing tens of kilograms. Its design quality directly affects the performance, safety, energy consumption and maintainability of the whole vehicle.
Why Understanding automotive wiring Harness Types Matters?
In modern automobiles, different systems (e.g., engine, lighting, air conditioning, security system, power windows and doors, infotainment system, etc.) have different technical requirements for the structural layout, electrical performance, and protection level of the wiring harness. For example, the wiring harnesses in the engine compartment must be high temperature resistant and oil-proof; while the wiring harnesses used for sensors should have low signal interference and high transmission stability; the wiring harnesses used for EV high-voltage systems should even have high voltage resistance and multiple shielding.
Failure to select the right type of automotive wiring harness for a specific system during harness selection or design can lead to a variety of serious problems:
- Safety hazards: Voltage mismatch or insulation failure may lead to short circuits and fires;
- Deterioration of performance: inadequate anti-interference performance of signal wires, resulting in abnormal response of the control system;
- Difficulty in maintenance: irrational structure of the wiring harness, chaotic wiring, difficult to overhaul and replace at a later stage.
Therefore, fully understanding and correctly selecting the type of automotive wiring harness is not only the basis for the design and modification of the entire vehicle, but also a key factor in guaranteeing the reliability of the electrical system and enhancing its service life and maintenance efficiency.

Main Automotive Wiring Harness Types
Different types of automotive wiring harnesses serve different vehicle subsystems and vary in materials, construction, connectors, and mounting methods. Understanding the basic classification of these harnesses therefore helps in the design, selection, modification, diagnosis and maintenance of various vehicle systems. Using the wrong type of wiring harness can lead to safety hazards, electrical failures, or significantly increased repair costs.
1️⃣ Chassis Wiring Harness
The chassis wiring harness is responsible for connecting various key components in the chassis area of the vehicle. For example, ABS system, wheel speed sensors, electronic parking, fuel level sensors, steering signals and so on. As it runs through the entire underbody of the vehicle, it involves the longest and most branching wiring harnesses, and therefore requires a high degree of structural protection and environmental resistance.
This type of wiring harness is often exposed to mud, water vapor, large temperature differences and severe mechanical vibration in the environment, so it is usually used with bellows outer protection, with a high level of protection (such as IP67) connectors. Especially near the wheels, exhaust system or frame edges, if they are not adequately secured or protected, they are susceptible to breakage or short-circuit problems caused by friction or corrosion.
Common construction/cable specifications:
- Wire Diameter: 0.5 mm² ~ 2.5 mm²
- Sheath: Bellows + Waterproof Heat Shrink Sleeve
- Connector: Waterproof AMP/Delphi connector (IP67+)
Vulnerable areas:
- Near wheel hubs, brakes, floorboard edges, susceptible to mud and vibration.
- Loose plug or cracked sheath may cause ABS alarm or light failure.

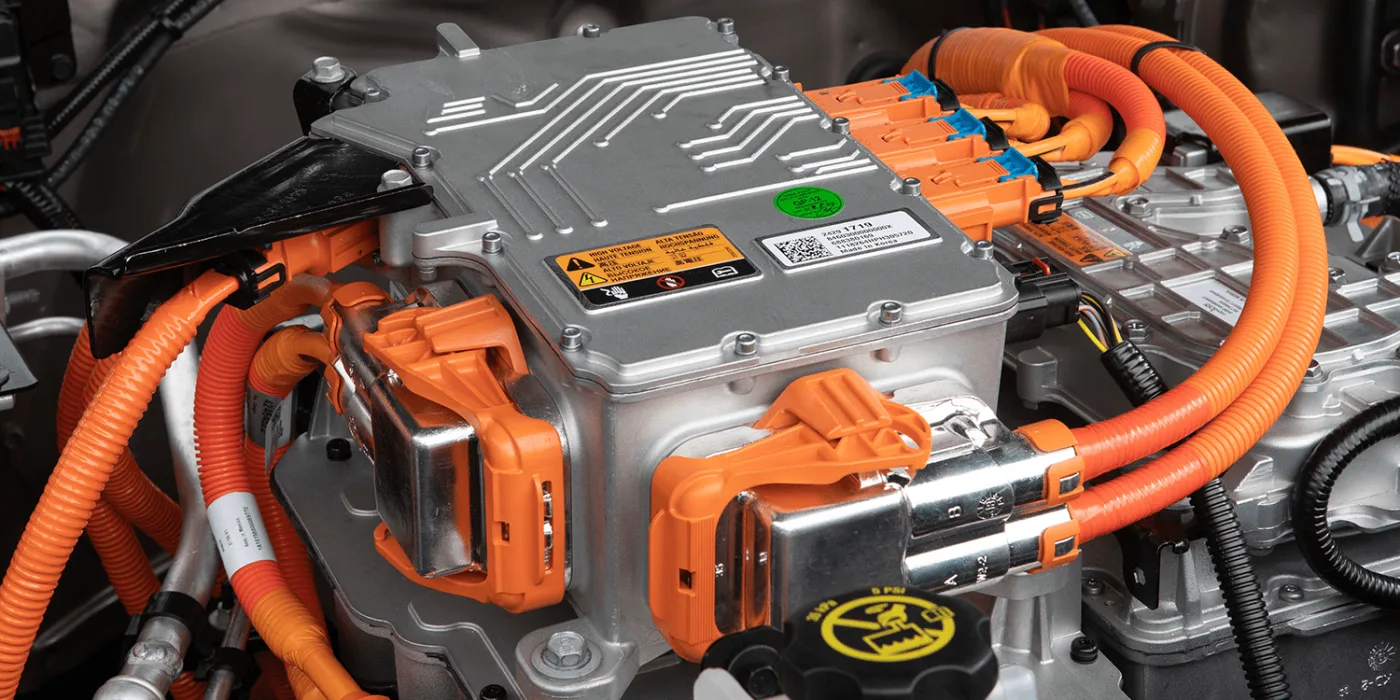
2️⃣ Engine Wiring Harness
The engine wiring harness connects the various electronic control and actuation systems of the engine and is the most central power system wiring of the entire vehicle. It connects the equipment including ignition system, fuel injector, throttle, fan, sensors (such as camshaft, crankshaft position), intake and exhaust control components.
The working environment of this type of automotive wiring harness is extremely harsh. It needs long-term exposure to high temperatures, oil, high-frequency vibration, and the operating temperature can reach 125 ~ 150 ° C. Therefore, commonly used high-temperature insulating materials (such as XLPE or Tefzel), and the use of precision crimping and locking dustproof connectors. If the wiring harness is not wired reasonably close to the exhaust pipe, it is very easy to damage the insulation layer due to heat, causing electrical failure or unstable performance.

Commonly used construction/cable specifications:
- Wire diameter: 0.75 mm² ~ 4.0 mm² (according to current demand)
- Insulation material: XLPE, Tefzel and other high temperature resistant materials
- Connectors: Locking type + dust and oil-proof sealing structure
Vulnerable area:
- Close to the exhaust pipe or engine block, easy to wear out due to high temperature aging or vibration.
- Wire harness and metal edge contact points, if not properly fixed or wrapped, easy to wear through the insulation layer
3️⃣ Dashboard / Instrument Panel Harness
The instrument panel wiring harness is responsible for connecting all electrical devices in the center console area, including the instrument panel, air conditioning control, switch panel, center screen, cigarette lighter, power outlet, etc., and is one of the most densely wired areas in the vehicle. Its wiring layout is directly related to the driver’s interaction experience and in-vehicle control logic.
Due to space constraints, this type of wiring harness requires fine wiring and silent handling. Therefore, it is often organized using flexible wires, color or heat shrink numbered wires, and cloth tape wraps. If forcibly squeezed and bent during installation or maintenance, it is easy to cause false connections, loose plugs and other problems, affecting the instrument display or power output.
Common construction/cable specifications:
- Wire Diameter: 0.22 mm² ~ 1.5 mm²
- Color coded wire or numbered heat shrink sleeve
- Sheath: cloth tape wrap or lightweight braided mesh for noise and vibration reduction (NVH)
Vulnerable Areas:
- Cable bends, loose tabs during instrument panel removal and installation
- Localized overheating when power outlet is overloaded
4️⃣ Front / Rear Lighting Harness
The front and rear light harness connects the entire vehicle’s lighting system. It includes headlights, fog lights, taillights, brake lights, reverse lights, turn signals and so on. These wiring harnesses are relatively independent, clearly distributed and easy to wire, but have many exposed locations and are greatly affected by the environment.
In order to ensure the stability and response speed of the lighting system, the front and rear light harnesses need to have good voltage transmission performance and sealed connection structure. However, if the cable breaks in the tail light area due to frequent door opening and closing, or the plug loosens and enters water, it will cause the light to flicker, burn bulbs and other malfunctions.

Common construction/cable specifications:
- Wire Diameter: 0.75 mm² ~ 1.5 mm²
- Sheathing: Bellows + Quick-lock plugs
- Relay/fuse module can be integrated
Vulnerable areas:
- Tail light wiring harness crosses the tailgate hinge, which is prone to breakage due to repeated switching.
- False or poor contact due to pulling on the plug during bulb replacement.
5️⃣ Door Wiring Harness
The function of the door wiring harness is to connect the power windows, power door locks, speakers, welcome lights, central locking and other equipment inside the door. This type of harness is typically a “dynamic harness” because it bends and stretches every time the door is opened and closed.
These harnesses must be highly flexible and fatigue resistant. That’s why manufacturers use highly flexible PVC or highly bend-resistant copper core wires with serpentine routing and specialized bellows protection. As the repeated activities at the door hinges are most likely to lead to wire breakage or abrasion, the common window control failure in old cars, multi-functional door control system failure stems from this.
Common construction/cable specifications:
- Wire diameter: 0.35 mm² ~ 1.0 mm²
- Specialized flexible sheathing (e.g. highly flexible PVC)
- Folded serpentine construction + bellows protection
Vulnerable areas:
- Door hinges are most prone to wire breakage or short-circuiting.
- Multi-channel door control system for high-end models, which is more complicated to investigate after damage.
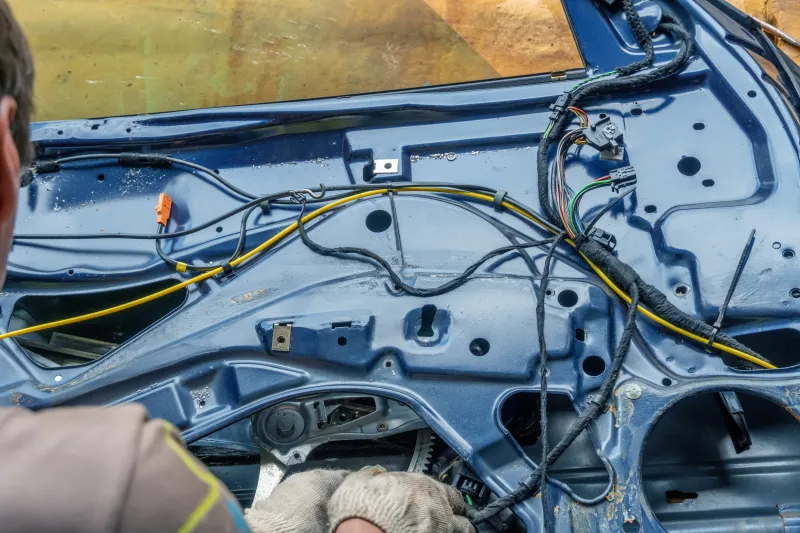

6️⃣ Roof / Ceiling Harness
Roof wiring harnesses are used to connect sunroof motors, dome lights, reading lights, ambient lighting, and interior microphones. Roof wiring harness is usually buried inside the roof, which requires high wiring aesthetics and light weight. It is both a functional wiring harness and part of the comfort configuration.
Because of the limited space up top, roof cables are usually thin gauge, lightweight wires that are taped to the roof liner. However, if the cable is cut by mistake when the roof is removed or if the wiring harness is corroded by water due to a leaking sunroof rail, it is very likely to cause an electrical short circuit or light failure.
Common construction/cable specifications:
- Wire diameter: 0.22 mm² ~ 0.75 mm²
- Usually multi-core thin wires with color coding
- Mostly fixed with adhesive tape + plastic crimps
Vulnerable areas:
- Cables mistakenly cut or pulled off during roof dismantling
- Corrosion and short circuits caused by water vapor entering the sunroof guides.
7️⃣ HVAC Wiring Harness
The air conditioning system wiring harness connects the blower, evaporator control, solenoid valves, temperature/humidity sensors, etc. and is a key component to the temperature control and air conditioning adjustment functions in the vehicle. It is usually located inside the center console or under the passenger side.
Such harnesses need to transmit both power and weak signals, so they are often equipped with shielded wires or twisted pair structures to avoid electromagnetic interference. Since its location is usually close to water vapor and condensing environments, a poorly sealed connector or loose wiring can lead to problems such as blower failure, uneven airflow, or air conditioning that doesn’t cool.
Common construction/cable specifications:
- Wire diameter: 0.35 mm² ~ 1.5 mm²
- Internally paired stranded or shielded wires for data line connections
- Teflon/XLPE insulation for high temperature protection
Vulnerable areas:
- Loose or poor contact between control panel and main harness plugging area
- Prolonged moisture or condensation corrosion of cable ends
8️⃣ Battery & Starter Harness
Battery and starter system wiring harness is the core wiring harness of the vehicle’s main power supply system. It connects the battery, starter motor, main fuse box, generator and other key parts, and is responsible for the delivery of high current, which is a high energy load type.
These harnesses often use thick conductors (6mm² or more), highly flexible and heat-resistant jackets, and are bolted or fused to ensure a stable electrical and mechanical connection. The most common problems include poor contact with the battery poles, heating of the cables due to ageing, or insufficient starting current, which in severe cases can lead to fuses or burns.

Common construction/cable specifications:
- Wire diameter: 6 mm² ~ 35 mm² or even thicker (mains power cable)
- Copper stranded wire, some high-end projects use tinned copper or aluminum alloy
- Sheathing: Double-layer heat-shrink tubing or high-strength braid.
Vulnerable areas:
- Loose or poor contact of battery poles leads to ignition and oxidation.
- Long-term high-current starting of the starter cable leads to heat aging.
OEM vs. Custom Automotive Wiring Harnesses
In automotive electrical system design and wiring solution selection, “OEM wiring harness” and “custom automotive wiring harness” are two common supply methods. Each of them has its own focus and is widely used in different project scenarios. Understanding their core differences will help engineers, purchasers or modification users make more reasonable choices based on project requirements.
OEM wiring harness refers to the standardized wiring harnesses mass-produced by OEMs or designated suppliers in accordance with the factory standards for new car assembly, after-sales maintenance or replacement. It has a high degree of repeatability and consistency.
Custom car Wiring Harness is a wiring harness solution designed and manufactured exclusively for a specific vehicle, project or function according to the parameters, space constraints, electrical configurations, etc. provided by the customer. It is particularly suitable for non-standard systems, modified vehicles or high performance vehicles.
| Category | OEM Wiring Harness | Custom Wiring Harness |
|---|---|---|
| Production Mode | Mass production with fixed molds | Small batch or one-off production with flexible layouts |
| Compatibility | Fits original vehicle structure only | Adaptable to any retrofit, modification, or non-standard setup |
| Design Flexibility | Fixed specifications, not modifiable | Fully customizable based on project needs |
| Cost Structure | Low unit cost, reliant on volume | Higher unit cost, suited for high-value applications |
| Function Expandability | Generally non-expandable | Supports integration of new modules (e.g., CAN, relay boxes) |
| Materials Used | Standard PVC wires, common connectors | Optional Tefzel, tinned copper, IP69-rated connectors, etc. |
| Target Users | OEMs, dealerships, aftermarket repair centers | Retrofit shops, engineers, R&D teams |
Examples of application differences:
✅ OEM Example:
A Volkswagen Golf 2020 with a faulty OEM taillight wiring harness. The customer can order the original wiring harness directly from the 4S store and replace it without modifying the design or adapting additional features.
✅ Customization Example:
The customer converted a 1967 Mustang to electric, adding electric air conditioning, touch gauges, and a center screen. The OEM does not provide a compatible wiring harness at all, so the control system wiring needs to be redesigned and CAN bus, BMS interface, etc. needs to be integrated.
automotive wiring harness types by application
According to the functional requirements of different vehicle systems, automotive wiring harness can be further subdivided into a number of specialized use categories. Each category of wiring harness not only connects different components, its design ideas, material selection, electrical performance and physical protection requirements there are also significant differences. The following are some of the most common types of wiring harnesses categorized by application:
- Interior car wiring Harnesses: Interior wiring harnesses are responsible for connecting electrical devices inside the vehicle. They are located inside the dashboard, seats, roof and door panels. It is characterized by a thin wire diameter and color coding.
- Powertrain car wiring Harnesses:It is one of the most central categories of wiring harnesses in the vehicle. It is not only responsible for the transmission of high currents, but also includes several critical sensor signals.
- Car Body Harnesses: The car body harnesses connect the various modules of the car body functions. They are one of the most widely distributed and diverse harness systems in the vehicle.
- Safety System Harnesses: Safety system harnesses connect the core active and passive safety equipment. Its reliability requirements are much higher than other systems, belonging to the “safety-critical wiring harness”.
- Infotainment Harnesses: Infotainment harnesses are one of the core experience systems of modern smart cars. This type of harness involves a large number of low-voltage signal transmission, some modules also need to support high-frequency high-speed transmission (such as LVDS, HDMI, USB3.0). Shielded twisted pair, data communication line, fiber optic and other structures are often used to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and to protect signal integrity. Its design focuses on stable connection, accurate communication, and high space utilization, which is especially suitable for intelligent cockpits, luxury cars and new energy vehicles.
- EV & Hybrid Harnesses: The wiring harness structure of new energy vehicles is significantly different from that of traditional models, with a large number of high-voltage, high-current and energy management-related wiring.
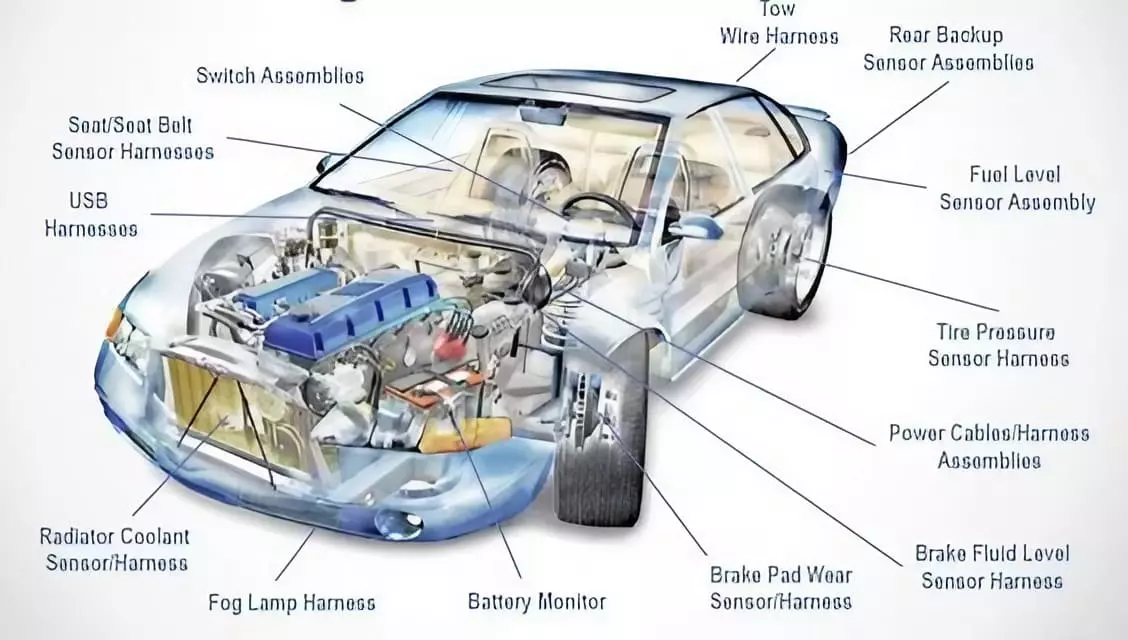
automotive wiring harness types by environmental protection
Automotive working environment is complex and variable, different harnesses need to withstand the temperature, humidity, dust, electromagnetic interference, mechanical shock and other conditions vary significantly. For this reason, the harness will be designed according to the required environmental protection level for classification.
- Standard Car Wiring Harness: Suitable for use in room temperature, dry, low load, interior space.
- Waterproof Car Wiring Harness: Suitable for use in areas exposed to the elements, car washes, and standing water.
- High-Temperature Car Wiring Harness: Suitable for use in engine compartments, near exhaust systems, electric compressors, high-performance race cars, and other high-temperature areas (ambient temperature >125°C).
- Shielded Car Wiring Harness: Suitable for use in areas requiring high-frequency, high-speed signal transmission or severe electromagnetic interference.
- Heavy-Duty / Rugged Harness: Suitable for use in harsh outdoor environments, heavy equipment, mining machinery, military vehicles and other extreme use occasions.
future trends in wiring harness technology
With the continuous development of automobiles towards intelligence, electrification, network connectivity and light weight, the traditional wiring harness system is experiencing rapid and profound technological changes. Wiring harness is no longer just a simple “power carrier”, but is evolving into a data communication hub, system integration platform, intelligent module carrier. The following are the main trends of current and future automotive wiring harness.
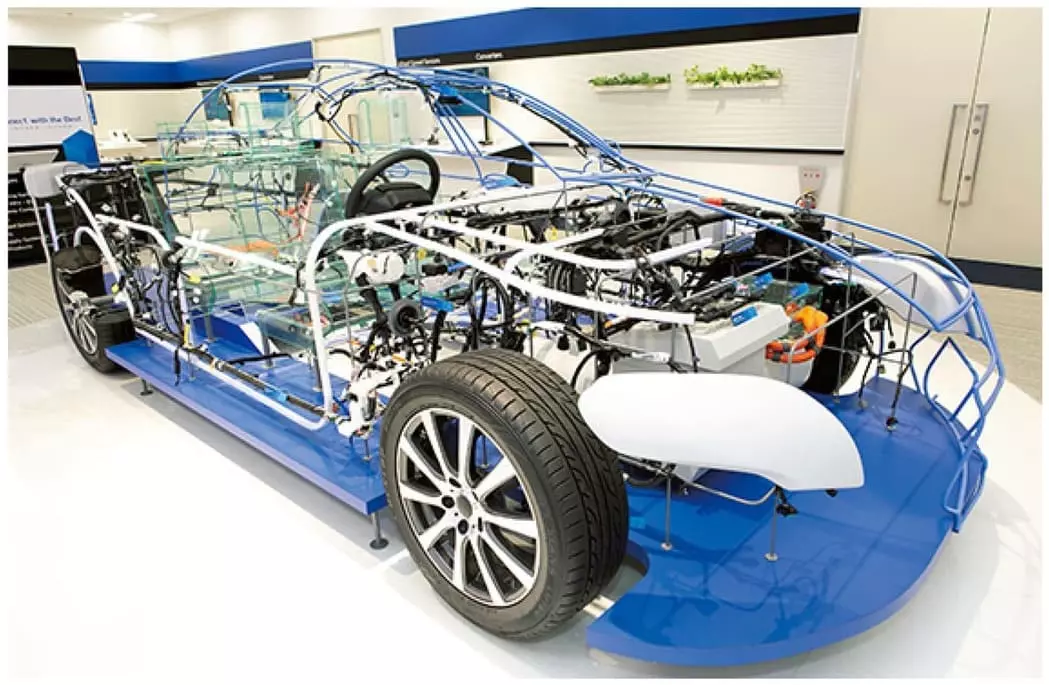
Trend 1 : High Integration Across Vehicle Systems
Whereas in the past each system (power, light, entertainment, safety) was individually wired with separate harnesses, the way forward is modular + centralized wiring. For example, CAN bus, Ethernet communication, power supply, inductive signals, etc. are integrated into a multi-core main harness, which significantly reduces the total number of wiring harnesses.
This approach can effectively improve vehicle wiring efficiency and reduce complexity and maintenance costs. It is an excellent approach for new platform architectures such as smart cockpits, autonomous driving platforms and software-defined vehicles (SDVs).

trend 2 : Lightweight Wire Harness Design
As new energy vehicles and electric platforms continue to increase their requirements for range and vehicle energy efficiency, lightweighting of wiring harnesses has become an important issue. Traditional copper conductors are gradually being replaced by aluminum alloy wire, thin-walled insulated wire, flexible flat cable (FPC/FDC) and other lightweight alternative materials.
In addition, the layout of the wiring harness also tends to be flattened and space-intensive. By reducing redundant wiring and optimizing the branch structure to achieve the purpose of weight reduction. Lightweight wiring harness can play a direct role in promoting the weight reduction of the whole vehicle, and the effect is significant in electric vehicles and high-performance sports cars.
trend 3 : Support for High-Speed Communication
In modern automobiles, systems such as ADAS, in-vehicle cameras, radar, LIDAR, etc. rely heavily on high-bandwidth communications. Traditional CAN/LIN communication can no longer meet the demand, Automotive Ethernet and FlexRay and other high-speed bus technology is becoming mainstream.
This promotes the development of wire harnesses with shielded structures, twisted cores, and low crosstalk designs. This can ensure the stable transmission of high-speed signals in complex electromagnetic environments, and become a key technical support for the realization of intelligent driving and Internet-connected vehicles.
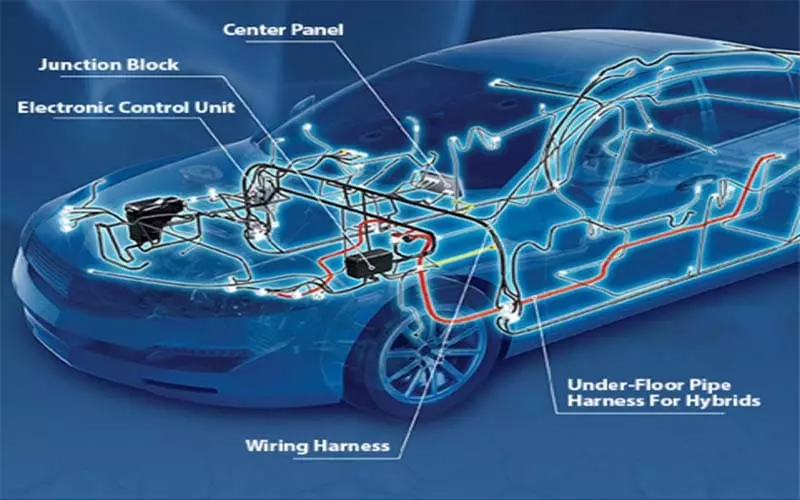
trend 4 : High Voltage & Multi-Voltage Coexistence
With the rapid popularization of Electric Vehicles (EV), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV), etc., the whole vehicle has appeared to have the structure of multiple voltage systems coexisting, such as:
- Main power system: 400V / 800V high voltage system
- Conventional low voltage system: 12V / 48V
- Auxiliary systems: Medium voltage systems for charging, air conditioning, heating systems, etc.
Wiring harnesses must be structured in such a way that high and low voltages are isolated and different systems are managed safely. This places higher demands on wire insulation, connector voltage resistance, electrocution design, and thermal management structures.
trend 5 : Modular & Pluggable Harness Architecture
Future wiring harnesses tend to be modular in design, connecting to the central trunking via plug-in sub-harnesses. This allows for quick installation, local replacement and flexible expansion. This is similar to the “electrical building block” model, which allows manufacturers to quickly combine different configurations.
This trend also applies to the aftermarket and customized vehicles, which can greatly improve harness maintenance efficiency and reduce spare parts costs. It also supports vehicle feature iterations or system upgrades.
Choosing the Right automotive Wiring Harness Type
With the increasingly complex structure of automobiles and highly integrated electronic systems, wiring harnesses are no longer just a simple combination of cables, but a key infrastructure for vehicle performance, safety and maintainability. In this paper, we have sorted out the main types of automotive wiring harness, including chassis harnesses, engine harnesses, instrumentation harnesses, door harnesses, etc., combined with the application scenarios, typical structures, common problems, to provide readers with a systematic cognitive framework.
In the face of wiring harness selection issues, should not blindly apply the standard configuration, but should be based on specific vehicle types (cars, SUVs, RVs, electric vehicles, etc.), electrical load requirements (signaling, power, high-voltage), and the degree of functional integration (whether or not to include CAN/LIN, multi-module control, intelligent diagnostics, etc.) comprehensive considerations. In modification, customization or high-performance projects, choosing the right type of wiring harness not only improves system stability, but also greatly facilitates later maintenance and expansion.
📌 Suggestion: Before designing or selecting the type, it is best to consult a professional wiring harness engineer with experience or a reliable car wiring harness manufacturing supplier, so that the wiring harness can be transformed from “usable” to “usable, easy to use and sustainable”.

What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
Table of Contents Wh

What is RJ45 Connector?
Table of Contents In

Top 10 LVDS Cable Manufacturers in World 2026
Table of Contents In

How to Check Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents In




