Design Rules for Automotive Wiring Harnesses
Home » Design Rules for Automotive Wiring Harnesses
Design rules for automotive wiring harnesses. Among the wiring harnesses, the design of automotive wiring harnesses is very demanding. Therefore there are many design rules that need to be followed.
This blog describes in detail the criteria for automotive wiring harness design rules, the core parameters, and the rules for each area of the design.
What Is Automotive Wiring Harness Design?
Automotive Wiring Harness Design refers to the engineering process of systematic planning, selection, configuration and wiring modeling of wires, cables, connectors, terminals, sheaths, layout paths, etc., according to the requirements of the electrical and electronic systems of the vehicle. It involves electrical engineering, structural design, thermal management, EMC anti-interference, safety regulations and other cross-cutting areas. Therefore, automotive wiring harness design is very important for vehicle development. Extremely important part.
Commonly speaking, the wiring harness is like the “neural network” and “vascular system” of the car. This component connects and powers all electronic equipment, including the engine control unit (ECU), instrumentation, lighting, audio, radar, camera, air conditioning system and so on. If the design is good, the whole car will run stably; if it is not designed properly, there may be frequent short circuits, fault codes, signal interference, and even safety hazards.

Why Does It Matter?
Both OEM manufacturers, wiring harness suppliers, as well as tuning teams and system integrators should attach great importance to the professionalism and standardization of wiring harness design.
- The infrastructure of the entire vehicle electrical system: wiring harnesses are no longer just for transmitting power, but also for a large number of data transmission tasks.
- Determine the safety and stability: unreasonable wiring harness design may bring serious consequences.
- Influence assembly efficiency and later maintenance: Excellent wiring harness design can significantly improve the wiring and maintenance efficiency of the whole vehicle.
- Determine the vehicle cost and mass production feasibility: a well optimized wiring harness design can directly affect the vehicle manufacturing cost and market cycle.
key standards and rules for automotive wiring harness design
Automotive wiring harness design is not only an engineering decision, but also a standard-driven process. Compliance with standards is a prerequisite to guarantee the safety, functionality and controllable quality of the whole vehicle. In international cooperation, OEM projects, and export business, compliance with automotive wiring harness design rules is more of a bottom line that cannot be compromised.
📌As a professional automotive wiring harness manufacturer, Linkwings’ technical team will clarify the regulations and technical standards of the market or customer at the early stage of design.
Common design rules for automotive wiring harness are as follows:
- I. ISO / TS 16949: Global Quality Management System Standard for the Automotive Industry
- Ⅱ. SAE J1128: U.S. automotive wire performance standards
- Ⅲ. IPC / WHMA-A-620: cable and harness assembly acceptability standards
- Ⅳ.RoHS / REACH: EU environmental regulations (Restriction of Hazardous Substances and Chemicals Management)
- V. OEM internal standards (Customer-Specific Requirements, CSR)
Other Commonly Referenced Standards in Wiring Harness Design
| Standard | Description | Application Scope |
|---|---|---|
| UL758 | Safety standards for wire and cable used in electronic equipment | U.S. market exports, product safety certification |
| GB/T 12528 | Chinese national standard for automotive low-voltage cables | Domestic Chinese automotive manufacturing |
| SAE J1742 | Performance testing for automotive electrical connectors | Connector development and validation |
| ISO 6722 | International standard for road vehicle cable structure and performance | General-purpose automotive wire design |
core parameters to consider before designing car wiring harness
Automotive wiring harness design does not start with “pulling a wire”. Rather, it is an engineering process of systematic planning after understanding a number of parameters such as vehicle system architecture, functional configuration, environmental conditions and performance requirements. Only in the early stages of design to fully consider these core parameters, in order to ensure that the later wiring harness has good safety, reliability, manufacturability and maintainability.
The following are the core parameters that must be evaluated before the design of automotive wiring harnesses:
1️⃣ Electrical Parameters
This is the basis for harness design. The voltage, current, load type and transmission distance of each circuit need to be clear.
- Voltage level: 12V, 24V, 48V (low voltage system), 400V, 800V (EV high voltage system), etc.
- Current carrying capacity: determines the cross-section area of the wire (e.g. AWG 16 is suitable for up to 15A).
- Voltage drop control: Long-distance transmission requires calculation of voltage drop to prevent abnormal operation of terminal equipment.
- Load type: power load (motor, light) or signal load (sensor, bus)
Design tip: Use Ohm’s law V=I × R in combination with wire length and conductor resistivity to calculate voltage drop.
2️⃣ Environmental Conditions
The environment in different wiring areas (engine compartment, roof, chassis, interior) varies significantly. Therefore, it is necessary to choose the corresponding insulation material and sheath structure.
- Temperature ratings: such as the engine compartment needs to withstand 125150 ° C, the interior wiring harness can be used 70105 ° C materials
- Moisture/flooding protection: Chassis and tailgate areas require IP67 or higher water resistance.
- Oil/chemical contact: TPE, XLPE, Teflon and other corrosion-resistant materials are recommended.
- UV/sun exposure: UV resistant sheathing materials should be selected for the wiring harness outside the vehicle
3️⃣ Spatial layout and installation path (Routing & Packaging Constraints)
The spatial arrangement of the wire harness directly affects the feasibility of assembly, the life of the harness and the aesthetics. Therefore, it is necessary to plan the route in advance with the 3D model.
- Routing path length and bending radius restrictions
- Pre-setting of holes, tie points, and clips.
- Avoid contact with high temperature/vibration components
- Plug terminals must be mounted in the direction of the operating angle.
4️⃣ System Topology & Features
The wiring harness design needs to be based on the electrical architecture of the vehicle. Define the location and communication relationship of each control unit (ECU), sensor, and actuator.
- Centralized vs Distributed ECU Architecture
- Node layout and topology of CAN/LIN/Ethernet buses.
- Modularized wiring scheme (e.g. seat module, door control module)
- Whether to reserve interfaces for future function expansion
📌 Design Tip: Try to modularize function-related lines to reduce cross-area routing and facilitate commissioning and maintenance.
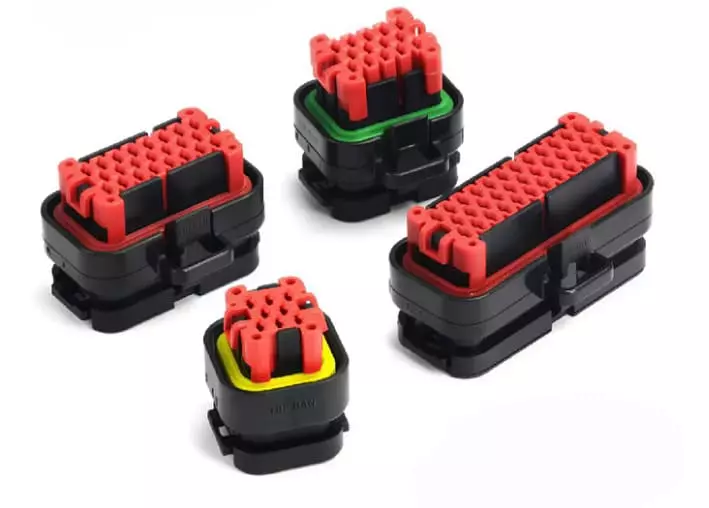
5️⃣ Connector and Terminal Specifications
Every wire eventually needs to be mated to a connector or terminal. Therefore it must be confirmed before design:
- Connector type (AMP, TE, Delphi, Yazaki, etc.)
- Number of poles and interface layout (male and female, locking structure)
- Crimping specifications and compatible wire diameter range
- Terminal current capacity and temperature rating
6️⃣ EMC / EMI Considerations
As more and more signals are present in modern vehicles, interference immunity has a direct impact on safety and user experience and needs to be planned during the design phase:
- Signal lines (CAN, LIN, LVDS) and power lines isolated wiring
- Twisted pair construction, shielding, single/double grounding design
- Avoid wiring parallel to high current lines or sources of electromagnetic interference.
7️⃣ Assembly & Serviceability
Wiring harnesses are not “design and finish”, but must also take into account the convenience of the manufacturing and maintenance phases.
- Whether the direction of the connector is easy to operate assembly tools
- Availability of marking systems such as heat-shrink labels, laser coding, etc.
- Whether branch modules can be replaced or maintained separately
- Whether the alignment interferes with disassembly or obscures other components
📌 Design Tip: Excessive complexity or cross-wiring can significantly increase man-hours, and it is recommended that the design phase be evaluated in tandem with the assembly process engineers.
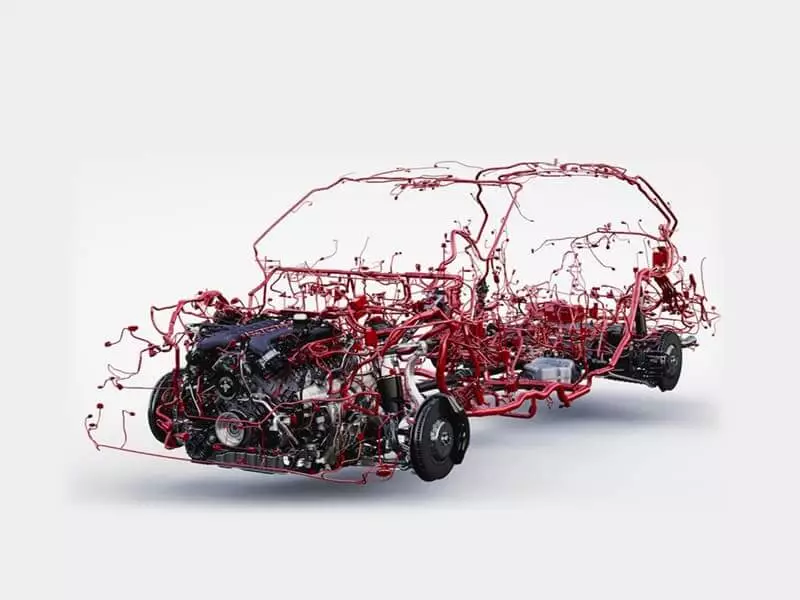
Routing and Layout Rules for Automotive Wire Harnesses
In wiring harness design, path planning is a crucial step. It not only determines the efficiency and clarity of the wiring of the entire vehicle, but also directly affects the feasibility of assembly, space utilization, safety, anti-interference ability and the difficulty of maintenance. Good path planning and wiring layout is the key to the success of a set of highly reliable wiring harness system.
The design of the wiring harness path should first be based on the vehicle structure and electrical system architecture, to clarify the location, function and communication relationship of all electronic devices. Therefore, designers need to have a clear understanding of the starting point and end point of each branch harness. And according to the body layout of the reasonable arrangement of the direction of the wiring, to ensure that the wiring harness in the transmission efficiency and wiring length to achieve a balance. If it is in a space-constrained area, the shortest and safest path must be used to avoid crossings, knots or repeated traversals.
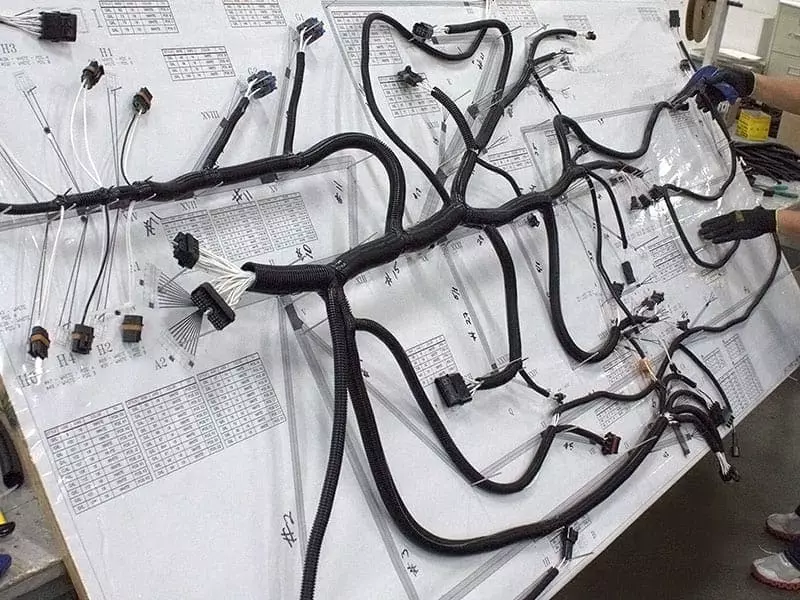
In the wiring process, should follow the “high voltage away from low voltage, power avoid signal, strong power avoid weak power” basic principles. This can minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI). For example, CAN bus, LIN bus, camera video lines, radar data lines and other key signal lines should be avoided and high-current power supply harness parallel arrangement. If necessary, metal shielding, ground isolation or twisted structure to strengthen the anti-interference ability.
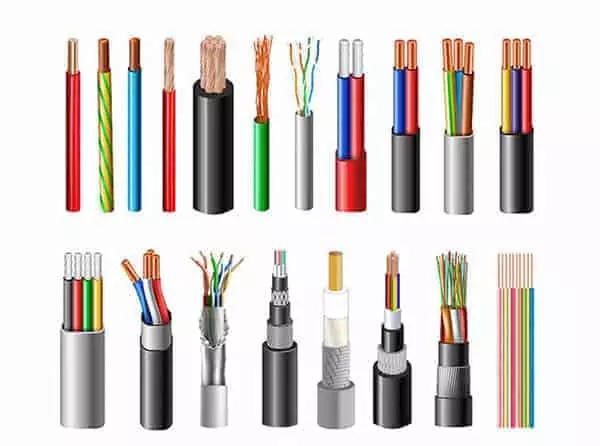
wire selection and gauge calcution rules
Wire selection and wire gauge determination is the most technical and error-prone part of the entire automotive wiring harness design.
It not only affects the electrical performance of the whole vehicle system, energy consumption control, but also directly determines the thermal stability, safety and manufacturing cost of the wiring harness. Selecting the wrong type of wire or calculating the wrong wire diameter will not only cause excessive voltage drop and equipment failure, but also may lead to overheating, corrosion, short circuit and other safety risks.
In the actual design, the first thing to do is to calculate the electrical current-carrying capacity according to the operating current, voltage level, and wire length of each circuit. The conductor is not the thicker the better, but to meet the premise of current-carrying capacity, taking into account the space wiring, flexible bending and cost control.
For example, a main power cable driving a fan may need to carry 20A, so if the length is more than 2 meters, you need to use 2.5mm² or thicker wires, and check whether the voltage drop exceeds the 5% system tolerance. On the other hand, even if the CAN/LIN bus signal line is farther away, a thin wire of 0.22~0.35mm² is generally sufficient due to the very low current.

Connector and Terminal design best practices
In the automotive wiring harness system, connectors and terminals are the “drop point” of the electrical connection, which is also one of the parts with the highest failure rate. A reasonable structure, reliable crimping, interface matching high degree of connection program is to ensure the reliable operation of the entire vehicle electrical system basis. Regardless of how complex the vehicle’s electronic system is, ultimately all energy and signals must enter the controller, sensor or execution through the terminals.
The design of connectors and terminals in automotive wiring harnesses is not just a matter of realizing a “plug-in” connection. It is also the key node that determines whether the entire vehicle electronic system can operate stably for a long time, whether it can resist environmental interference, and whether it is easy to repair and replace. Whether it is the whole vehicle wiring or modular wiring harness integration, connection reliability is always the most important bottom line for designers to protect.
An excellent connector/terminal design program should strike a balance between mechanical structure, electrical performance, environmental adaptability and manufacturability. Only by following the standards, matching materials, rational layout, and strict crimping, can we create a wiring harness system with high reliability, low failure rate, and strong scalability.

protection and insulation design requirements
Automotive wiring harnesses usually work in high temperature, high humidity, vibration, dust and other complex environments, so they must have good mechanical protection and electrical insulation.
Protection design mainly includes the use of bellows, braided mesh, heat shrink tubing, tape, cloth tape and other sheath materials. The purpose of this design is to protect the wire harness from abrasion, pinching or corrosion. Insulation design requires that the outer jacket material of the wire has sufficient temperature, pressure and aging resistance, such as PVC, XLPE, Teflon and so on.
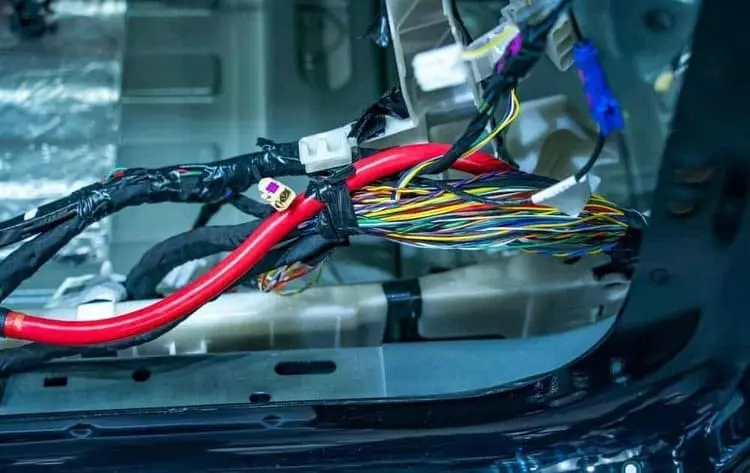
Good protection and insulation not only prolongs the life of the harness, but also effectively prevents safety hazards such as short circuits, leakage and fire. And in high-risk areas, the use of high-grade (e.g. IP67/IP69K) protection solutions should be prioritized.
separation of power and signal lines: Best Practices
In the automotive wiring harness design, signal lines and power lines must be reasonably distributed, physical isolation. To avoid electromagnetic interference (EMI) affects system stability. Power lines carry large currents, easy to CAN, LIN bus, camera, radar and other low-voltage signal lines produce interference. This problem is more likely to occur in parallel wiring or space-dense areas.
Therefore, the design should try to let the signal lines and power lines layered wiring, cross rather than parallel lines. In addition to this, add shielding where appropriate or use twisted pairs to protect signal integrity. Critical systems (such as ADAS, audio, communication modules) are recommended to use independent harness channels to ensure reliable and safe data transmission.
EMI Shielding and grounding strategies in harness design
EMI can directly affect the radar, camera, ECU, wireless communication and other systems in the automobile. Therefore, effective shielding and grounding measures should be incorporated when designing automotive wiring harnesses. Common practices are as follows:
- Use shielding (e.g., aluminum foil, copper braid) to wrap signal wires.
- Proper grounding (single- or double-ended) to release interfering signals.
The grounding strategy is also critical to ensure that each module has a stable, low-impedance ground loop. Avoid the formation of “ground loops” or signal noise interference. In high-speed communications (e.g. Ethernet, LVDS) and safety systems, good EMC design is key to ensuring the stable operation of the entire vehicle electronics system.
Conclusion: designing a safe, reilable and scalable car wiring harnesses
In this guide, “design rules for automotive wiring harnesses”, we take a comprehensive look at the key rules for automotive wiring harness design.
From wire selection, wiring layout, connector crimping, to signal isolation, protection design, standards and specifications, to system-level EMC control and modularization strategies. It can be seen that wiring harness design is not just a combination of pulling wires and plugs, but a highly engineered, standardized and verifiable system work. It is directly related to the vehicle’s electronic system stability, safety, assembly efficiency and after-sales maintenance convenience.
Whether it’s a new OEM project development, an aftermarket system retrofit, or a custom wiring harness for a special purpose vehicle. It is important to collaborate with experienced harness engineers or specialized suppliers in the early stages of design. By working together to confirm key parameters, interface specifications and wiring logic, we can reduce risk at the source and improve the overall project success rate.
Linkwings has more than ten years of experience in automotive wiring harness design and has provided perfect automotive wiring harness design solutions for more than 200 customers worldwide!

What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
Table of Contents Wh

What is RJ45 Connector?
Table of Contents In

Top 10 LVDS Cable Manufacturers in World 2026
Table of Contents In

How to Check Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents In



