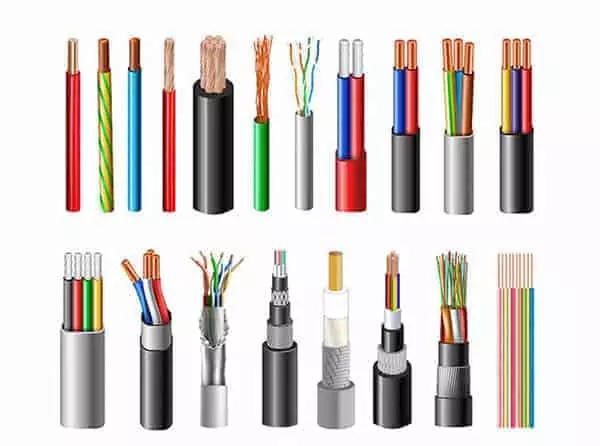
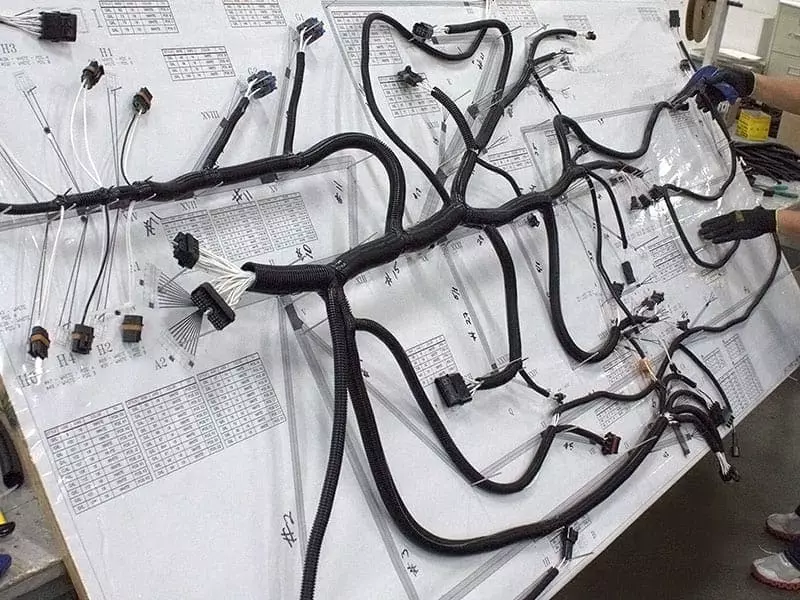
Types of Wires Used in Wiring Harness
Home » Types of Wires Used in Wiring Harness
In modern electrical systems, wiring harnesses are a critical component for the efficient transmission of power and signals. One of the key concerns for users during the design and manufacturing process is the types of wires used in wiring harnesses. Different types of wires not only determine the performance and reliability of the harness but also directly impact its application effectiveness in industries such as automotive, industrial equipment, medical, and aerospace.
This blog will provide a detailed analysis of common wire types and their characteristics from a professional perspective, helping you make more scientific and safer decisions during the selection process.
What are the wires in a wiring harness?
In electrical and electronic systems, a wiring harness is a highly integrated connection system. It combines multiple wires, terminals, connectors, and protective components to enable efficient transmission of power and signals. The “wires” in a wiring harness are not just ordinary cables, but carefully selected electrical connection carriers based on their function, electrical performance, insulation requirements, and mechanical properties.
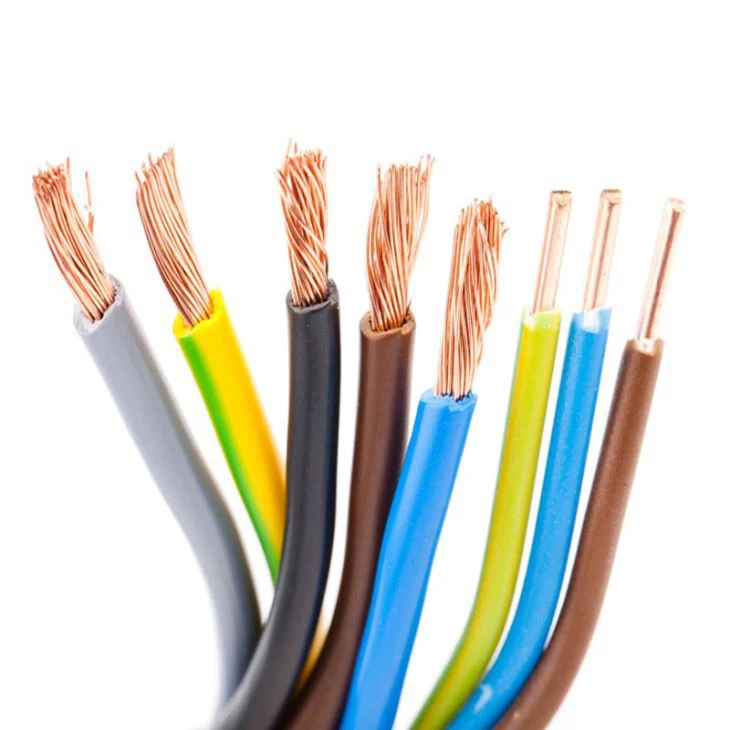

Definition and Function
The wires in a wiring harness are the “blood vessels” of the entire system, responsible for transmitting electrical power and information from one node to another. Unlike a single cable, the wires in a wiring harness often have specific functions:
- Some are used for high-current power supply (such as power lines).
- some are responsible for low-level signal transmission (such as sensor lines).
- and others are responsible for high-speed data transmission (such as communication lines).
Therefore, when designing a wiring harness, wire selection must consider electrical safety, mechanical durability, and application scenario compatibility.
Differences from ordinary cables
Wires in a wiring harness are fundamentally different from single cables. They require more rigorous selection and integrated design, primarily in the following aspects:
- Multi-core combinations: A single wiring harness may contain dozens or even hundreds of wires of different specifications, which must be arranged reasonably to avoid signal interference and electromagnetic coupling.
- Insulation and sheathing design: Different insulation materials (such as PVC, XLPE, Teflon) are selected based on environmental conditions, and additional sheathing or braided layers are added to enhance abrasion resistance, temperature resistance, and chemical resistance.
- Protection rating: Industrial and automotive wiring harnesses often require IP67 or higher waterproof and dustproof capabilities to ensure stable operation in harsh environments.
- Terminal compatibility: Wires must be strictly matched with terminals, connectors, and other components; otherwise, it will affect contact resistance, durability, and overall electrical performance.
Common Wiring Harness Wire Types
In the design and manufacture of wiring harnesses, the selection of wires is a critical factor in determining performance and reliability. Different types of wires have their own advantages in terms of electrical characteristics, mechanical strength, weather resistance, and cost, and must be matched to the specific application environment. Below, we introduce the types of wires commonly used in wiring harnesses from several common perspectives:
1. Classification by conductor material
Bare Copper Wire
- Offers excellent conductivity and flexibility, making it the most common choice for wire harness conductors.
- Suitable for conventional electrical connections in automobiles, industrial equipment, and home appliances.
Tinned Copper Wire
- Coated with a layer of tin on the copper conductor surface to enhance oxidation resistance and corrosion protection.
- Suitable for wiring harnesses exposed to humid or salt fog environments, such as marine and outdoor equipment.
Aluminum Wire
- Lightweight, suitable for applications with strict lightweight requirements (such as automotive and aerospace).
- However, it has weaker mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, typically requiring an additional protective layer.
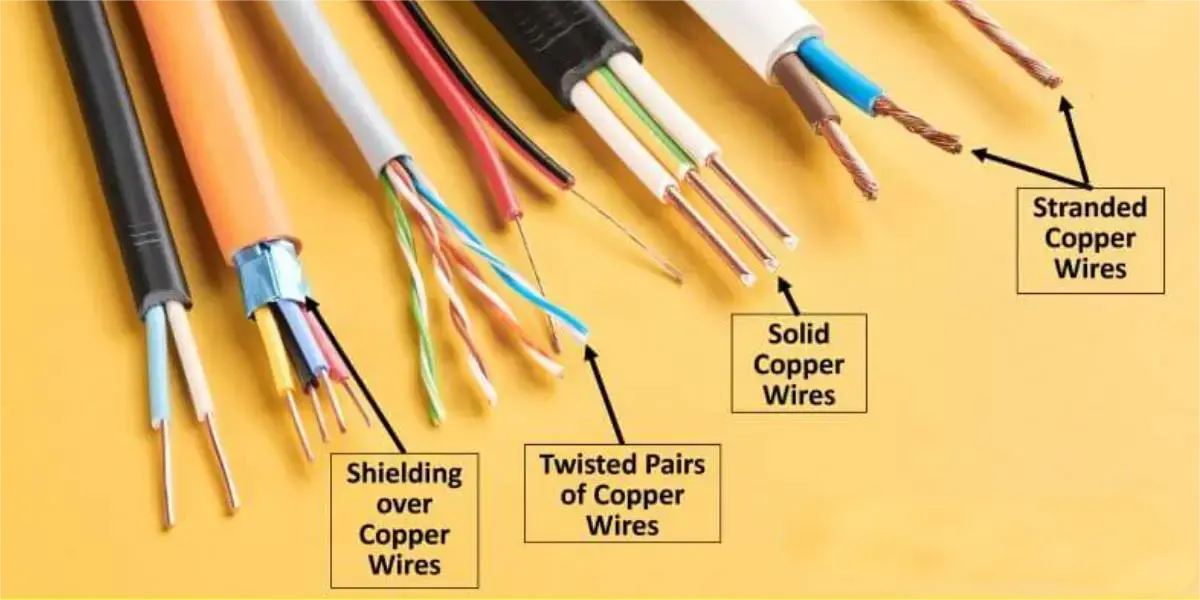
2. Classification by Insulation Material
PVC Insulated Wire (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- Low cost, moderate flexibility, and basic insulation and weather resistance.
- Commonly used in low-voltage electrical systems, such as automotive wiring harnesses and consumer electronics.
XLPE Insulated Wire (Cross-linked Polyethylene)
- Excellent high-temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, and mechanical wear resistance.
- Commonly used in power transmission, industrial automation, and new energy equipment.
Teflon/PTFE/FEP Insulated Wire
- Withstands extreme high and low temperatures (-200°C to +250°C) and chemical corrosion.
- Widely used in aerospace, military, and medical equipment.
Silicone Insulated Wire
- High flexibility, suitable for environments requiring repeated bending, while offering excellent high and low temperature resistance.
- Commonly used in robotics and industrial automation equipment drag chain wiring harnesses.
3. Classification by Electrical Function

Power Wires:Used for high-current transmission, such as motor and battery pack connections.
Signal Wires:Used for low-level signal transmission, such as sensors and control systems.
Data & Communication Wires:Includes twisted pair cables, CAN bus cables, and Ethernet cables, used for high-speed data transmission and network communication.
Coaxial Cable:Suitable for radio frequency and high-frequency signal transmission, such as cameras and antenna systems.
Shielded Wires:Features an outer shielding layer to reduce electromagnetic interference, commonly used in industrial control and medical equipment.
4. Classification by industry standard
Automotive wire (SAE/ISO standard): Meets requirements for high temperature resistance, vibration resistance, and fuel resistance.
Aviation wire (MIL-Spec Wire, such as M22759): Ultra-lightweight, high temperature resistance, radiation resistance, suitable for extreme environments.
Industrial Cables (UL/CSA Standards):Meets specifications for industrial automation and electrical control cabinets, commonly used in factories and energy sectors.
Medical Device-Specific Cables:Features biocompatibility, disinfection resistance, and high signal integrity to ensure long-term stable operation of medical devices.
Wire Selection Guide for Wiring Harness
When designing and manufacturing wiring harnesses, the correct selection of wires is a key factor in ensuring system safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Different applications have different requirements for the electrical performance, mechanical properties, and environmental adaptability of wires, so a scientific and systematic selection process is necessary.
Key factors to consider when selecting a model
- Current/voltage rating
- Environmental conditions
- Mechanical stress
- Standards and certifications
- Cost control
When designing and manufacturing wiring harnesses, the selection of conductors is a critical step in ensuring system safety and reliability. A reasonable selection process must take into account multiple factors. First, the current and voltage ratings determine the conductor cross-sectional area and insulation rating, which are the most basic starting points. If the selection is inadequate, it may lead to conductor overheating or insulation failure; if the design is excessive, it will result in material waste and increased costs.
Second, environmental conditions are equally critical. The temperature, humidity, and potential chemical corrosion in the environment where the wiring harness is located directly impact the service life of the wires. For example, high-temperature environments require the use of heat-resistant materials such as XLPE or Teflon insulation, while applications exposed to prolonged moisture or salt fog conditions are better suited for tin-plated copper wires or wires with special protective sheathing.

Additionally, mechanical stress must not be overlooked. Vibrations common in automotive and aerospace equipment can cause fatigue damage to wires, while wiring harnesses in robots and automated equipment must be able to withstand repeated bending without affecting electrical performance, making flexibility and wear resistance key considerations.
Meanwhile, standards and certifications are also indispensable components of the selection process. Automotive wire harnesses must comply with SAE or ISO standards, industrial wire harnesses typically follow UL or CSA certifications, aerospace and military applications rely on MIL-Spec grade wires, and medical devices must meet biocompatibility and electrical safety standards. Beyond performance and standards, cost control is another factor that must be balanced in practical applications. By avoiding overdesign while ensuring safety and reliability, a win-win outcome can be achieved in both technical and economic terms.
Common Application Scenarios and Recommended Cable Solutions
Automotive Industry: We recommend using automotive-grade cables compliant with SAE/ISO standards, which are heat-resistant and vibration-resistant, suitable for engine compartments and body control systems.
Medical Equipment: We recommend using Teflon/PTFE or medical-grade silicone cables, which offer high signal integrity, resistance to disinfectants, and high/low temperature resistance, ensuring stability in medical environments.
Industrial Robots: We recommend using high-flex drag chain cables, which are resistant to bending and wear, ensuring long-term dynamic operation without damage.
Renewable Energy (Photovoltaic/Wind Power): We recommend XLPE or specialized photovoltaic cables, which are resistant to UV rays, high temperatures, and humid heat, suitable for long-term outdoor harsh environments.
Linkwings' professional advantages in wire and wire harness selection
Professional Engineering Team
Linkwings has a team of experienced electrical and mechanical engineers. We can accurately recommend suitable wire and harness types based on customers’ current and voltage requirements, environmental conditions, and industry standards, and provide scientific design solutions.
Cross-Industry Experience
We have successful case studies in multiple fields, including automotive, medical, industrial automation, energy, and aviation. We are also familiar with international standards such as SAE, ISO, UL, CSA, and MIL-Spec, enabling us to quickly complete compliant designs and enhance product market adaptability.

Strict Quality Control System
All wires and wire harnesses undergo multiple tests for electrical performance, mechanical strength, and environmental adaptability before leaving the factory. Linkwings strictly controls material selection and production processes to ensure product stability and reliability in high-temperature, vibration, humid, or corrosive environments.
Customization Capabilities
In addition to providing standardized solutions, Linkwings can also offer personalized customization based on customers’ specific needs. From prototype development, sample verification to mass production, we provide customers with full-process technical support and flexible manufacturing capabilities.
Customer Value Orientation
Through scientific selection and reliable manufacturing, Linkwings helps customers reduce system risks and enhance overall reliability. We also balance cost control and delivery schedules to ensure that customers’ projects are implemented safely and efficiently.
FAQs
1) What is the most common type of wire used in wiring harnesses?
Answer:
Copper-core multi-strand wires are the primary type, with typical examples including automotive-grade GPT/GXL/TXL (SAE J1128), industrial/equipment-grade UL AWM (UL 758), and shielded twisted signal wires (e.g., CAN, Ethernet twisted pairs). Reasons: excellent conductivity, flexibility, fatigue resistance, and mature termination processes.
2) Is copper or aluminum wire better for wiring harnesses?
Answer:
Copper wire is generally the better choice. Copper has approximately 1.6 times the electrical conductivity of aluminum, better corrosion resistance and solderability/crimpability, smaller dimensions, and higher contact reliability. Aluminum wire has the advantages of being lightweight and inexpensive, but requires a larger cross-sectional area.
3) What are some insulation materials suitable for high-temperature environments?
Answer:
- PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene)/FEP/PFA: 200–260 °C, chemical-resistant, low friction, commonly used in aerospace/military applications.
- ETFE: ~150–200 °C, cut-resistant, wear-resistant, commonly used in aviation/automotive interiors.
- XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene): 125–150 °C, commonly used in automotive interior main lines.
- Silicone rubber: -60–200 °C, soft, flexible, used in complex wiring/vibration conditions.
- Polyimide (PI, Kapton): ≥200 °C, radiation/high-temperature resistant, used in aerospace electronics.
Selection should consider continuous/peak temperature, chemicals, abrasion resistance, flexibility, flame retardancy/smoke toxicity (e.g., UL94, EN 45545), etc.
4) Can a harness contain multiple types of wires?
Answer:
Yes, and it is quite common. For example: power wires (large cross-section), sensor/signal wires (shielded/twisted), communication wires (CAN, Ethernet). Design considerations:
- Layered/zoned wiring (separate high voltage/high current from weak signals, minimize crossing).
- EMI/EMC: Twisting, shielding, single/dual-ended grounding, 360° shielding crimping.
- Mechanical reliability: Minimum bending radius, jacket/corrugated tubing, abrasion-resistant jacket, stress relief.
- Consistent termination: Terminal/housing compatibility and unified crimping parameters.
5) How can we ensure that the wiring harness meets industry certifications (UL, SAE, MIL-Spec)?
Answer:
- Select certified materials/components: such as UL AWM wire, approved terminals and insulators; automotive-grade SAE J1128/ISO 6722 wire; military-grade MIL-DTL-22759, MIL-DTL-27500, etc.
- Follow assembly standards: IPC/WHMA-A-620 (Wire Harness Assembly Acceptability), qualified crimp height/pull-off force, and process cards.
- Type and production testing: continuity/insulation/withstand voltage (Hipot), contact resistance, tensile strength, thermal aging, humidity and heat, vibration, and salt spray; test according to UL, SAE, MIL-STD-810, etc., as required.
- Documentation and traceability: Bill of Materials (BOM), drawings, process records, first article/PPAP (automotive), calibration, and batch traceability; UL project number/document (E-Number) management.
- Third-party or customer audits: UL wire harness services, automotive IATF 16949 system, and aerospace AS9100 system audits conducted as required by the project.
Conclusion
The proper selection of wires is the foundation for building reliable wire harnesses, directly impacting the electrical performance, durability, and safety of the system. As a professional industrial wire harness manufacturer, Linkwings adheres to rigorous engineering methods and standards (UL/SAE/MIL-Spec/IPC/WHMA-A-620) to provide optimal wire selection and customized wire harness solutions for various application scenarios, including automotive, industrial automation, medical, and aerospace. Our services cover the entire process from material selection, EMI/EMC, protection and termination, validation testing, to mass production delivery.

What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
Table of Contents Wh

What is RJ45 Connector?
Table of Contents In

Top 10 LVDS Cable Manufacturers in World 2026
Table of Contents In

How to Check Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents In