What Are the Different Types of Flat Cables?
Home » What Are the Different Types of Flat Cables?
In modern electronic and industrial applications, flat cable types are a frequent focus for engineers and procurement personnel. Compared to traditional round cables, flat cables are widely adopted in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, medical devices, and industrial control systems due to their space-saving design, flexible bending capabilities, and ease of installation.
This article systematically introduces several common flat cable types, including FFC, FPC, ribbon cable, high-speed flat cables, and power flat cables. It helps readers gain a deeper understanding of their structural characteristics, performance differences, and application scenarios. Additionally, we provide practical selection guidance to ensure you can choose the appropriate cable for your project requirements. As a professional cable and connector manufacturer, Linkwings possesses extensive R&D and production expertise, offering both standardized and custom flat cable solutions to meet diverse client needs.
A flat cable is a type of cable where conductors are arranged in parallel and enclosed within a single insulating layer. Unlike traditional round cables, flat cables feature a more uniform geometric structure, with conductors arranged in a ribbon-like configuration, hence the common alternative name “ribbon cable.” This structure not only gives the cable its distinct flat appearance but also provides exceptional flexibility and compactness. It is highly suited to the demands of modern electronic devices for miniaturization, lightweight design, and high-density wiring.
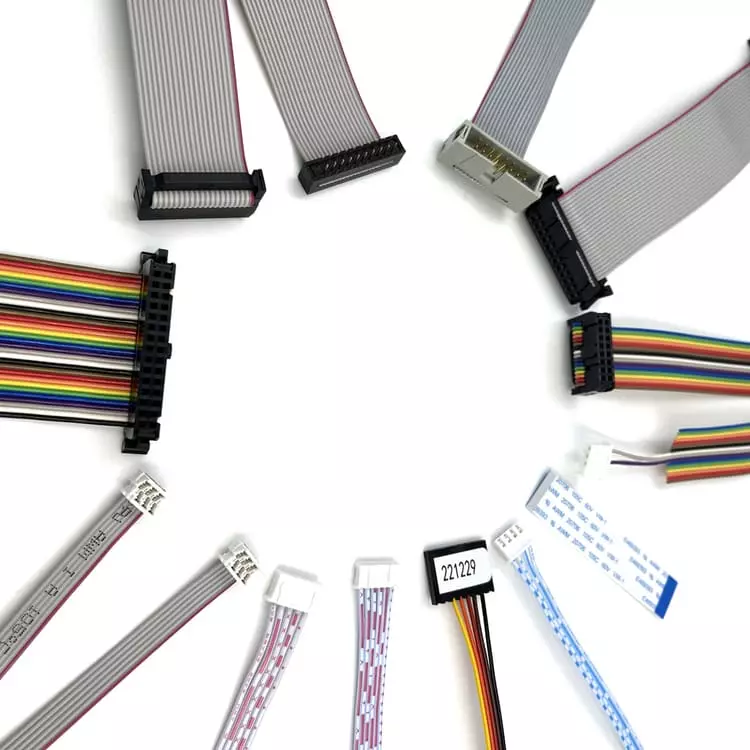

Structure and Characteristics
- Conductor Arrangement: Internal conductors are made of copper or tinned copper, strictly maintained in parallel alignment to ensure uniform electrical properties.
- Insulation Materials: Commonly PVC, polyester (PET), or polyimide (PI), which provide insulation while maintaining cable flexibility.
- Standard Pitch: Common pitches include 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 1.27mm, 2.0mm, and 2.54mm to accommodate various interface requirements.
- Flexibility and Bend Performance: Compared to round cables, flat cables are better suited for repeated bending and can even withstand 90° or 180° folds in confined spaces.
In short, flat cable represents a modern cable design that balances compactness, electrical performance, and flexibility. It not only meets the demands of increasingly complex electronic systems but also reduces manufacturing and maintenance costs. This is the fundamental reason why various flat cable types are widely adopted across industrial and electronic applications.
Main Different Types of Flat Cables
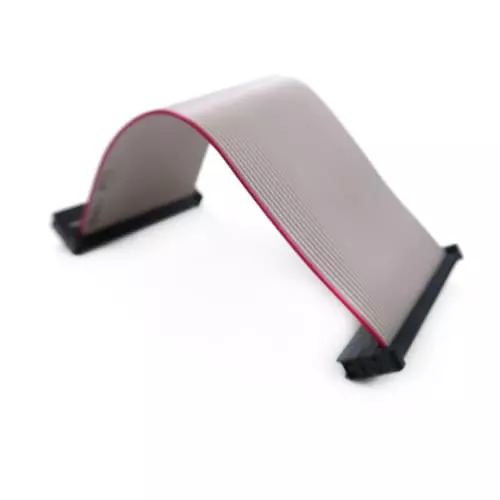

Definition: FFC is a flexible flat cable composed of multiple copper conductors arranged in parallel and encapsulated within an insulating layer (such as PET or PI film), resulting in an extremely thin and flexible appearance.
Features:
- Typically measures between 0.5mm and 1mm in thickness, making it exceptionally thin and lightweight;
- Conductors are uniformly spaced with common pitches of 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 1.25mm, and 2.54mm;
- Capable of 180° bending, making it suitable for confined spaces.
Applications:
Widely used in scenarios requiring highly flexible wiring, such as laptop display connections, printer scan heads, digital cameras, and automotive center consoles.
2. FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit)
Definition: FPC is a flexible circuit formed by chemically etching or laminating copper traces onto a flexible substrate (polyimide PI or polyester PET). It functions as both a cable and a printed circuit board.
.webp)
Features:
- Supports three-dimensional routing, offering greater flexibility than FFC;
- Capable of carrying complex circuits, not only transmitting signals but also integrating chips and components;
- High reliability with resistance to high temperatures and bending.
Applications:
Commonly used in areas requiring lightweight and high reliability, such as connecting smartphone motherboards to displays, medical monitoring devices, automotive radar modules, and wearable devices.

Definition: Ribbon Cable, also known as flat cable or ribbon wire, is a flat cable composed of multiple insulated conductors arranged in parallel. Commonly colored for easy identification.
Features:
- Pitch typically 1.27mm or 2.54mm;
- Typically used with IDC (Insulation Displacement Connectors);
- Enables simultaneous connection of multiple signals, suitable for standardized interfaces.
Applications:
Widely used in computer IDE hard drive interfaces, industrial controllers, test equipment, and communication modules, serving as a common wiring solution in traditional electronic products.
4. High-Speed Flat Cable
Definition: A flat cable optimized for high-speed signal transmission, typically featuring precise impedance control in its structure and employing shielding to reduce electromagnetic interference.

Features:
- Low crosstalk and low latency performance;
- Suitable for differential signal transmission (e.g., LVDS, HDMI, USB 3.0);
- Common structures include multi-layer insulation + shielding designs to ensure high-speed stability.
Applications:
Used in high-bandwidth scenarios such as data centers, 5G communication equipment, high-speed storage devices, and industrial high-speed sensors.
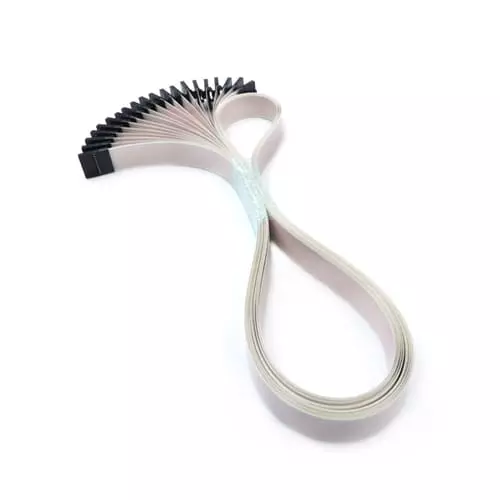

5. Power Flat Cable
Definition: A flat cable primarily used for power transmission, featuring a large conductor cross-sectional area and specifically designed to carry medium to high currents.
Features:
- Supports high-current transmission, suitable for power systems;
- Flat design enables efficient routing in confined spaces;
- Typically constructed with multiple copper conductors pressed side-by-side, offering excellent heat dissipation.
Applications:
Widely used in new energy vehicle battery modules, industrial power equipment, solar inverters, and other applications requiring high-current transmission.
Comparison of Different Types of Flat Cables
| Type | Features | Typical Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFC Flexible Flat Cable | Parallel conductors, thin and flexible | Laptop displays, printers, cameras, car infotainment | Lightweight, cost-effective, space-saving | Limited current capacity, not for high power |
| FPC Flexible Printed Circuit | Foldable, supports 3D routing, can integrate circuits | Smartphones, medical devices, automotive radar modules | Highly integrated, heat-resistant, durable | Higher cost, complex manufacturing |
| Ribbon Cable | Multi-core parallel wires, standardized pitch | Computer IDE interfaces, industrial controllers, communication modules | Easy mass connection, color-coded for identification | Bulky, not ideal for high-speed signals |
| High-Speed Flat Cable | Controlled impedance, low crosstalk, supports high-speed data | Data centers, 5G equipment, high-speed storage | Low latency, high signal integrity | Higher cost, strict process requirements |
| Power Flat Cable | Large conductor cross-section, supports high current | EV battery packs, industrial power, solar inverters | High current capacity, space-efficient, good heat dissipation | Limited flexibility, not suitable for repeated bending |
How to Choose the Right Flat Cable?
Selecting the appropriate flat cable requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as space, electrical performance, environmental adaptability, manufacturing processes, and cost.
1. Space and Structural Design Requirements
- If the product requires thinness, lightness, and space-saving features—such as laptops, cameras, or automotive center consoles—FFC is recommended.
- If the device has complex internal wiring, requires three-dimensional folding, or demands flexible design, FPC is more suitable.
- For standardized interfaces or modular designs, such as industrial controllers or test equipment, ribbon cables are a viable option.

2. Electrical Performance Requirements
- Signal Transmission: For high-speed data (e.g., HDMI, USB 3.0, LVDS signals), high-speed flat cables are recommended due to their controllable impedance and low crosstalk.
- Power Transmission: For applications requiring high current capacity (e.g., new energy vehicle battery modules or industrial power supplies), power flat cables are recommended;
- For low-power, low-current applications, FFC or ribbon cables suffice.
3. Environmental and Reliability Requirements
- High-Temperature Environments: Prioritize FPCs with polyimide (PI) insulation for superior heat resistance;
- Vibration Scenarios: For automotive electronics, select FPCs or high-quality FFCs with excellent contact reliability and bend resistance;
- Long-Term Stability: In medical or industrial settings, choose RoHS/REACH/UL-certified products to ensure safety and environmental compliance.
4. Production and Assembly Methods
- Bulk Assembly: Ribbon Cables paired with IDC connectors significantly enhance assembly efficiency;
- Automated SMT Processes: Opt for FFC/FPC in SMT packaging formats;
- Custom Manufacturing: If standard products fail to meet requirements, select Linkwings’ custom services based on pitch, row count, length, plating, and other specifications.

5. Cost and Supply Chain Considerations
- Mass-market consumer electronics: Cost-sensitive applications should prioritize standardized FFC or ribbon cables;
- High-end medical/automotive electronics: Applications demanding superior reliability and performance over cost should opt for FPC or high-performance, high-speed flat cables;
- Special projects: Consult Linkwings’ engineering team for customized selection support to prevent rework or increased maintenance costs due to mismatched components.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between FFC and FPC?
A1: FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) is a standard flexible flat cable with a simple structure, suitable for conventional signal transmission. FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) is a type of flexible circuit board capable of supporting complex circuits and enabling three-dimensional routing. It offers higher reliability and durability but also comes at a higher cost.
Q2: Can flat power cables replace round power cables?
A2: In certain applications, such as new energy vehicle battery modules or industrial power systems, flat power cables can serve as a viable alternative. They can handle high currents while offering space savings and superior heat dissipation. However, round cables remain the preferred choice in wiring environments requiring extreme flexibility.
Q3: What applications are high-speed flat cables suitable for?
A3: High-speed flat cables are suitable for scenarios requiring high bandwidth, low crosstalk, and signal integrity. Examples include data centers, 5G communication equipment, high-speed storage, and industrial sensors. They feature impedance-optimized construction and incorporate shielding layers to ensure the stability of high-speed signals.
Conclusion
As electronic devices continue to evolve toward thinner, faster, and more reliable designs, flat cables have become increasingly vital across diverse applications. Whether it’s FFC, FPC, ribbon cables, high-speed flat cables, or power flat cables, different types of flat cables address distinct requirements.
During the selection process, engineers and procurement personnel should comprehensively consider factors such as space, electrical performance, environmental conditions, manufacturing processes, and cost to ensure the chosen cable delivers long-term stable operation. As a cable and connector manufacturer with over 15 years of experience, Linkwings not only offers standardized flat cable products but also provides customized specifications and solutions tailored to customer requirements, accommodating diverse needs from small-batch prototyping to large-scale production.

What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
Table of Contents Wh

What is RJ45 Connector?
Table of Contents In

Top 10 LVDS Cable Manufacturers in World 2026
Table of Contents In

How to Check Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents In