What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
Home » What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
When it comes to network cabling or equipment selection, many engineers and procurement personnel encounter this question: What is the difference between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 connectors? This is a common challenge that frequently troubles users in practical work.
RJ45 connectors of different categories exhibit distinct differences in structure, performance, and suitable applications, directly impacting network speed, stability, and future scalability. This article comprehensively analyzes the distinctions between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 connectors—from foundational concepts and performance parameters to real-world applications—providing professional guidance for your selection process.
RJ45 Connector Basics
RJ45 is an 8P8C modular interface widely used in Ethernet cabling systems. It achieves stable data transmission by connecting to twisted-pair conductors through eight metal contacts.
The RJ45 connector serves as the physical interface between network cables and network devices. Its contact quality and design directly impact signal integrity, interference resistance, and overall network stability.

The Relationship Between RJ45 Connectors and Cable Categories
Although RJ45 connectors appear largely identical externally, their internal structure must correspond to the cable category. For example:
- Cat5e RJ45 plugs are compatible with Cat5e twisted-pair cables, rated for 100 MHz bandwidth and 1 Gbps transmission.
- Cat6 RJ45 plugs are compatible with Cat6 twisted-pair cables, supporting higher 250 MHz bandwidth while maintaining lower crosstalk at elevated frequencies.
Therefore, selecting an RJ45 connector that matches the cable category is essential to ensure optimal network link performance.
Differences in Network Performance Between Cat5e and Cat6
To truly understand the difference between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 connectors, one must first grasp the performance distinctions between these two types of network cables. This is because RJ45 connectors must match the cable category to ensure optimal link performance.
Cat5e (Enhanced Category 5)
- Bandwidth: 100 MHz
- Supported Rates: 1 Gbps (within 100 meters)
- Typical Applications: Home networks, standard office environments, video conferencing, and everyday data transfer
- Technical Features: Compared to Cat5, Cat5e improves crosstalk performance and enhances signal integrity, though it remains primarily designed for Gigabit Ethernet.
Cat6 (Category 6)
- Bandwidth: 250 MHz
- Supported Rates:1 Gbps (within 100 meters). 10 Gbps (within 55 meters, limited by crosstalk and attenuation)
- Typical Applications: Enterprise networks, data centers, HD video transmission, high-bandwidth office environments
- Technical Features: Cat6 features an optimized twisted-pair pitch design and enhanced isolation structure, significantly reducing Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT) and maintaining stability at higher frequencies.
| Feature | Cat5e Cable | Cat6 Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 100 MHz | 250 MHz |
| Supported Speed | 1 Gbps (up to 100 m) | 1 Gbps (up to 100 m); 10 Gbps (up to 55 m) |
| Typical Use | Home networks, office LANs, general data transfer | Enterprise networks, data centers, HD video, high-bandwidth environments |
| Crosstalk Performance | Improved over Cat5, suitable for Gigabit Ethernet | Enhanced design reduces NEXT, supports higher frequency transmission |
| Cost | Lower | Higher, but supports better performance |
What is the Difference Between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 Connectors?
1) Mechanical and Geometric Structure: Higher Frequencies → Stricter Geometric Control
Contact and Alignment Geometry
- Cat5e Plug/Socket: Designed for 100 MHz operating bandwidth, contact springs and plastic guides offer minimal “compensation” for high frequencies.
- Cat6 Plug/Socket: Designed for 250 MHz, often incorporates paired compensation geometries (cap/ind compensation), finer contact spacing, and height control to reduce NEXT/Return Loss.
Maintaining Pair Integrity
- Cat6 termination areas typically incorporate load bars/liners or internal isolation ribs, requiring shorter untwisted lengths (field installation recommendation ≤ 10–13 mm, shorter is better), significantly improving near-end crosstalk.
Form Factor and Connector Cavity
- To accommodate thicker conductors and insulation, Cat6 connectors feature larger rear ferrules and deeper wire guides. Cat6 Keystone/patch panel modules also incorporate a more substantial internal structure for compensation and isolation.
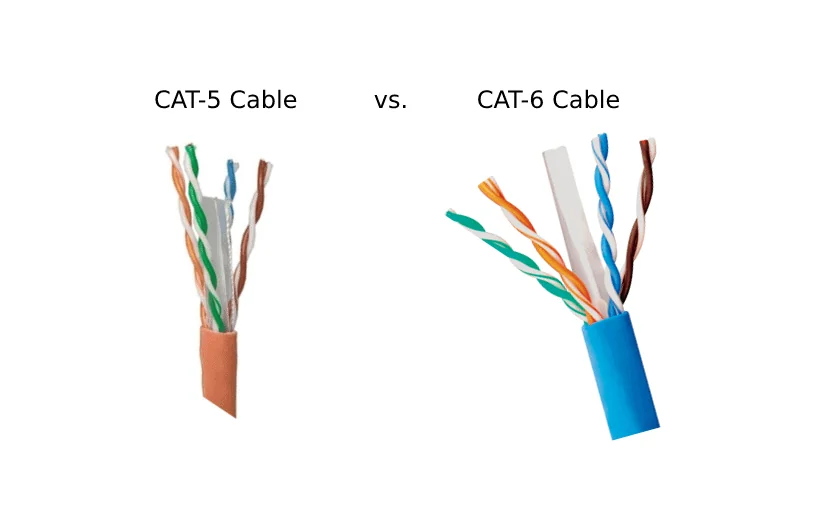
2) Supported wire gauge and insulation outer diameter: Cat6 accommodates larger conductors and thicker insulation
Conductor wire gauge (AWG)
- Cat5e plugs: Primarily 24 AWG (some compatible with 26/24).
- Cat6 Plug: Generally supports 23–24 AWG (some also support 22 AWG) to accommodate the thicker conductors common in Cat6/Cat6a.
Insulation OD and Cable OD
- Cat6 features thicker insulation and wider pair spacing, requiring larger OD compatibility for plug wire holes and crimping tools. Using Cat5e connectors on Cat6 cables risks insufficient crimping/springback, leading to poor contact and degraded RL performance.
3) Electrical Performance and Internal Compensation: Cat6 Optimized for 250 MHz
Bandwidth and Performance Focus
- Cat5e components are evaluated up to 100 MHz, with the primary focus on meeting Gigabit Ethernet NEXT/RL baseline requirements.
- Cat6 extends to 250 MHz, placing greater emphasis on controlling RL (Return Loss) and ANEXT (External Crosstalk) at higher frequencies.
Compensation Structure
- Cat6 jacks commonly feature metallized components/compensation steps that fine-tune near-end capacitance/inductance pairs to counteract inherent crosstalk within the jack. High-quality Cat6 keystones also incorporate PCB trace compensation.
Pass-through Plug Differences
- Minimal impact in Cat5e environments; however, for Cat6, uneven trimming creating “wire stubs” significantly degrades RL and high-frequency response. Inferior pass-through plugs are strongly discouraged in many Cat6 applications.
4) Materials and Plating: Lifespan and High-Frequency Contact Stability
Contact Gold Plating Thickness
- Cat5e typically features 6–15 µin Au;
- Cat6 favors 30 µin (or higher) to enhance insertion/removal lifespan and contact stability (actual specifications subject to manufacturer standards).
Spring Contact Material and Housing
- Cat6 imposes stricter requirements on spring contact elasticity retention (creep resistance) and contact resistance variation control; shielded types utilize metal housings to achieve 360° shield termination.

5) Shielding and EMI: Cat6 favors shielding or tighter shield termination
UTP vs. STP/FTP/S/FTP
- Both categories offer unshielded and shielded versions, but in high-density/high-interference/10G transition scenarios, Cat6/6a is more commonly paired with FTP/SFTP.
Shield continuity
- Cat6 shielded connectors emphasize 360° shield crimping and single-point grounding to reduce Alien Crosstalk and radiation.
6) Termination Processes and Tolerances: Cat6 Demands Greater Precision
Stripping Length and Twist Release Control
- Cat6 exhibits heightened sensitivity to stripping/twist release tolerances; even slight over-twist release amplifies NEXT in the 200–250 MHz range.
Conductor Type (Solid/Twisted)
- Cat5e plugs commonly feature three-prong/two-prong contact structures for solid/stranded conductors respectively; Cat6 plugs require strict conductor shape matching, with mismatches causing poor contact or contact resistance drift.
Load Bar/Conductor Arrangement
- Cat6 often requires load bars to secure wire sequence and depth, ensuring each pair maintains longer twist length and symmetry.

7) PoE and Thermal Performance: Thicker Conductors/Lower DC Resistance = Lower Temperature Rise
PoE Support
- Both specifications support PoE (802.3af/at/bt).
Temperature Rise and DC Resistance Imbalance (DCRU/DCR imbalance)
- Cat6 typically features thicker conductors, lower DC resistance, and reduced temperature rise. In bt Type 3/4 (60–90W) scenarios, Cat6 components offer superior control over temperature rise and common-mode noise.
8) Interoperability and Compatibility: System Performance = Weakest Link
“Backward Compatibility” Principle
- Using a Cat6 plug with Cat5e cable: Link performance remains limited by Cat5e;
- Using Cat5e connectors with Cat6 cable: Prone to failing RL/NEXT at 250 MHz, preventing Cat6 performance.
Full-Link Consistency
- Connectors, jacks, patch cords, trunk cables, and patch panels must share the same category and shielding strategy. Otherwise, the system will only perform at the lowest category level.
Quick Comparison: Cat5e vs Cat6 RJ45 Connectors
| Dimension | Cat5e RJ45 Connector | Cat6 RJ45 Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Target Bandwidth | 100 MHz | 250 MHz |
| Supported Conductor | Typically 24 AWG (sometimes 26/24) | 23–24 AWG (some designs support 22 AWG) |
| Internal Structure | Basic geometry, minimal compensation | With compensation structures/load bars, stricter geometry |
| Termination Tolerance | More forgiving, easier to terminate | Stricter (shorter untwist length, precise stripping) |
| Gold Plating | Typically 6–15 µin | Typically 30 µin or above (depending on vendor) |
| Shielding & EMI | Available in UTP/shielded; general EMI control | More often shielded; stronger EMI/ANEXT control |
| PoE Thermal Rise | Higher (thinner conductors, higher DCR) | Lower (thicker conductors, lower DCR) |
| 10G Suitability | Not recommended | Up to 55 m (Cat6a preferred for full 100 m) |
| Mix-and-Match Impact | Mixing with Cat6 lowers system to Cat5e level | Limited by cable performance if used on Cat5e cable |
Cat5e vs Cat6 RJ45 Connectors: Applications
| Applications | Cat5e RJ45 Connector Applications | Cat6 RJ45 Connector Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Home & Small Office | Build Gigabit LAN for browsing, video calls | Provides more stable 1 Gbps; suitable for multimedia/design studios |
| Cost-Sensitive Projects | Lower cost, easier termination, ideal for budget wiring | Higher cost but supports future upgrades, longer lifecycle |
| Security & Surveillance | Supports IP cameras and access control at Gigabit speeds | Supports HD/4K video surveillance with higher bandwidth and lower latency |
| Enterprise Network | Suitable for basic office LAN at 1 Gbps | Suitable for high-bandwidth office, partial 10GbE support (≤55 m) |
| Data Center / Server Room | Generally not recommended, only for low-cost temporary use | Supports 10GbE up to 55 m, ideal for servers and virtualization |
| High-Power PoE | Supports PoE/PoE+, but higher resistance | Thicker conductors, lower DC resistance; supports 802.3bt high-power PoE |
Cat5e RJ45 Connector Application Scenarios
- Home Networks and Small Offices: Ideal for establishing 100 Mbps or 1 Gbps local area networks, supporting daily office tasks, web browsing, video conferencing, and similar needs.
- Cost-Sensitive Projects: Cat5e RJ45 plugs and cables offer lower prices with relatively relaxed installation requirements, making them suitable for budget-constrained cabling projects.
- Basic Security and Surveillance: Supports standard gigabit-speed data transmission and PoE power delivery for IP cameras, access control devices, and similar equipment.
Cat6 RJ45 Connector Applications
- Enterprise and High-Bandwidth Office Networks: Suitable for environments requiring high stability at 1 Gbps or partial 10 Gbps short-distance connections, such as multimedia conference rooms or design studios.
- Data Centers and Server Rooms: Supports higher frequencies and lower crosstalk, delivering 10GbE links within 55 meters to meet big data and virtualization demands.
- HD Video and Multimedia Transmission: Suitable for wired transmission of 4K/8K video streams and AR/VR devices, ensuring high throughput and low latency.
- High-Power PoE Applications: In PoE+ or 802.3bt (up to 90W) power delivery scenarios, Cat6 RJ45 plugs and cables offer lower DC resistance and superior thermal dissipation.

How to Choose the Right RJ45 Connector?
When choosing between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 connectors, the most critical factors to consider are bandwidth requirements, application environment, and future scalability.
For home networks, small offices, or cost-sensitive projects, Cat5e RJ45 connectors adequately meet everyday 1Gbps requirements. In enterprise networks, data centers, or high-bandwidth scenarios like HD video transmission, Cat6 RJ45 connectors offer clear advantages with their higher 250 MHz bandwidth, reduced crosstalk, and support for 10GbE. Additionally, selection should consider shielding levels (UTP/STP), PoE power delivery capability, and compliance certifications (e.g., UL, RoHS, TIA/ISO) to ensure long-term stable performance and reliability of the network system.
FAQs
Q1: Is a Cat6 RJ45 plug backward compatible with Cat5e cable?
A1: Yes, a Cat6 plug can be crimped onto Cat5e cable. However, the final performance is still limited by the Cat5e cable itself, achieving only 100 MHz / 1Gbps.
Q2: Will mixing Cat5e and Cat6 connectors on the same network affect performance?
A2: Yes. The performance of the entire link is determined by the “lowest category.” If Cat6 cables and devices are used with Cat5e plugs or modules at any point, the overall performance will be downgraded to Cat5e levels.
Q1: Do Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 connectors look the same?
A3: They are visually very similar, both being 8P8C modular interfaces. However, Cat6 plugs feature larger internal space to accommodate thicker wire gauges and typically include strain relief tabs or isolation plates to reduce crosstalk.
Conclusion
Through this analysis, you should now clearly understand what is the differences between Cat5e and Cat6 RJ45 connectors. Their primary distinctions lie in bandwidth, supported speeds, structural design, interference resistance, and application scenarios. Cat5e is better suited for everyday Gigabit networks and cost-sensitive applications, while Cat6, with its higher 250 MHz bandwidth and support for 10GbE, is the preferred choice for enterprises and data centers.
When selecting a solution, consider your current needs, future scalability, and cabling standards holistically. If you require professional Cat5e/Cat6 RJ45 solutions, Linkwings offers internationally compliant products and customized services to ensure your network systems operate reliably and efficiently over the long term.

What is RJ45 Connector?
Table of Contents In

Top 10 LVDS Cable Manufacturers in World 2026
Table of Contents In

How to Check Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents In

How to Remove Lvds Cable?
Table of Contents Du